Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR)
$99 Base price View My Quote RequestFourier Transformed Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
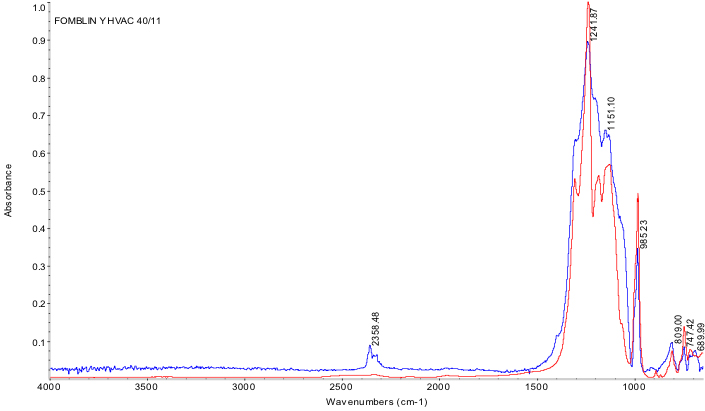
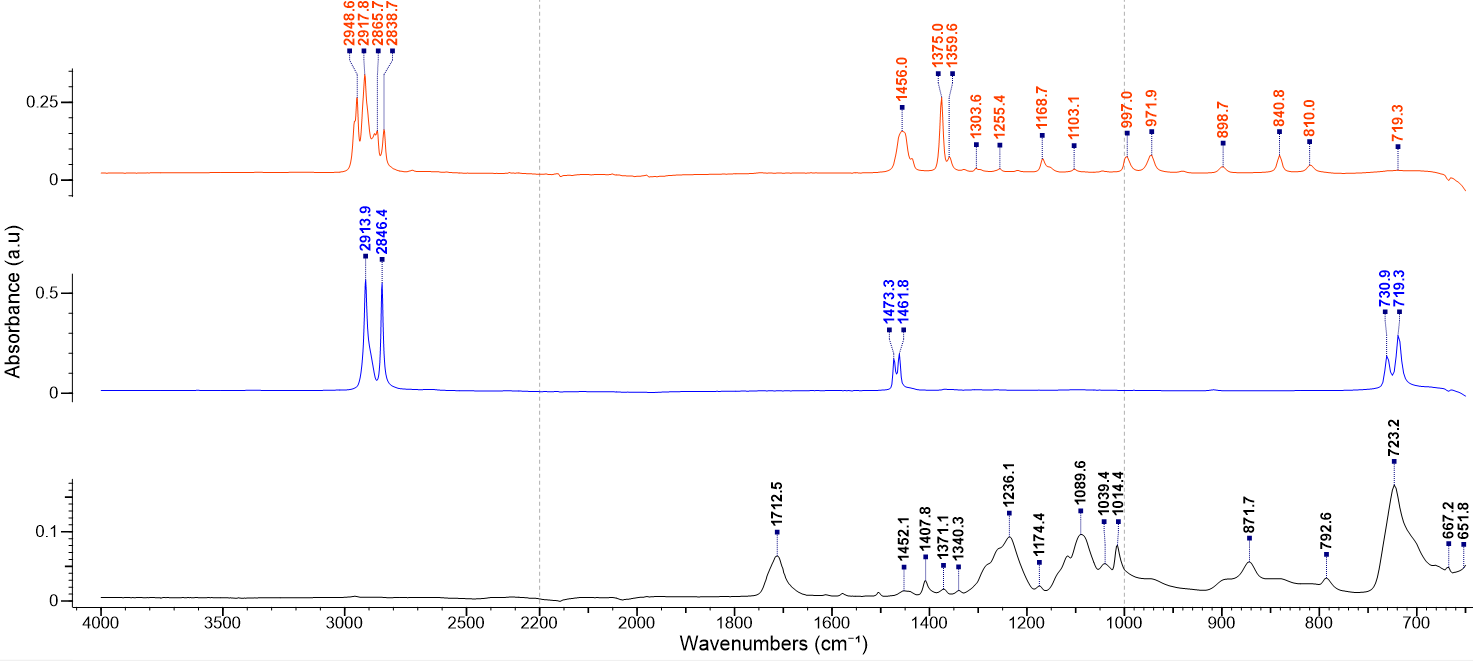
Fourier-transformed infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) is a nondestructive, optical technique used to analyze chemical composition and the optical properties of a material.
- Rapid results
- Nondestructive analysis
- Particularly well suited for organic chemical analysis
- Robust reference libraries are available
- Requires reference or a standard / control sample to make positive chemical identifications
- Most inorganic molecules do not exhibit an FTIR spectrum
Technical Specifications:
Learn More:

Thermo Scientific Nicolet iS50 IR Spectrometer
- Motorized and automated beamsplitter exchange
- Multiple Detectors with Flexible Spectral Range:
- Standard: 7800 – 350 cm-1
- Mid-IR Optical Resolution: < 0.09 cm-1
- Wavenumber Accuracy: better than 0.005 cm-1
- Flexible Analytical Modes
- View Instrument Brochure

Thermo Scientific Nicolet Continuum IR Microscope
- 32x magnification
- Multiple detector options:
- Narrow-band MCT-A: High performance 11700 – 750 cm-1
- Medium-band MCT-A: 11700 – 600 cm-1
- Wide-band MCT-B: 11700 – 450 cm-1
- Sampling Modes: transmission, reflection, grazing, and ATR
- View Instrument Spec Sheet

Thermo Fisher Nicolet 6700 IR Spectrometer
- 4 Analytical Modes / Measurement Accessories: transmittance; specular reflectance; Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR): both Ge and Diamond-C sampling systems; NicPlan IR Microscope (transmittance and reflectance mapping with 20 µm spot size)
- View Instrument Brochure
In an FTIR measurement, an initially wide range of infrared wavelengths are simultaneously shone upon an area of the sample.
Using an interferometer, the FTIR system then extracts a specific wavelength band at a time and measures its light intensity: selectively detecting either reflected or transmitted beams. The operator will determine whether to target transmittance or reflectance intensity based on the sample’s composition and topography. After this initial measurement, the extracted wavelength band is subsequently scanned over the entirety of the wavelength range, capturing an intensity measurement at each band. The resulting values are then fourier-transformed to produce the initial sample spectrum.
To isolate the real sample spectrum, a reference – or ‘blank’ – trial is conducted without any material inserted in the beam path. This spectrum is used to normalize the sample spectrum and to isolate the relevant specimen information from the total signal.
In the wavelength range of interest, different types of chemical bonds absorb at different wavelengths: providing a spectral signature which is material dependent. The resulting background-subtracted spectrum can then be used to qualitatively identify chemical functional groups and trace chemicals present in the specimen.
ATR-FTIR is a variant FTIR measurement mode which uses a specialized crystal to generate multiple internal reflections along the lateral dimension of the sample, increasing signal-to-noise and surface sensitivity.

Datasheet: Medical Device Characterization with the Covalent Platform

TGA-IR Analysis Using the OMNIC Mercury TGA Software

Contamination Identification
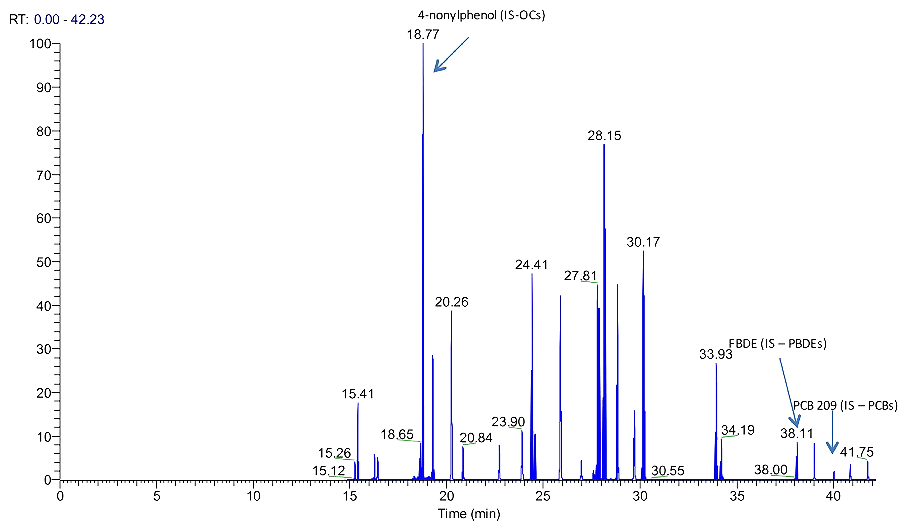
Gas Chromatography Mass Spectroscopy (GCMS)
GCMS is performed to generate a quantitative representation of the chemicals present in a sample. It can be...
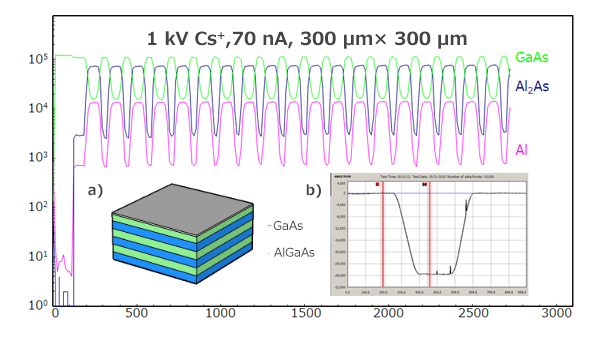
Time of Flight Secondary Ion Mass Spectroscopy (ToF-SIMS)
Time of flight secondary ion mass spectroscopy (ToF-SIMS) is a highly surface-specific analytical technique used to qualitatively assess...
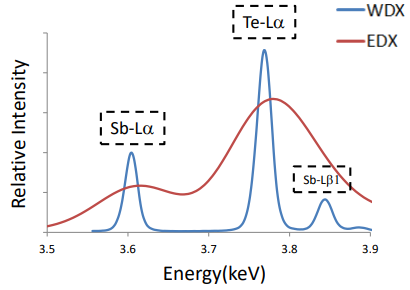
Wavelength Dispersive X-ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy (WDXRF)
Wavelength dispersive x-ray fluorescence spectroscopy (WDXRF) is a non-contact, non-destructive technique used to measure elemental composition, elemental concentration...
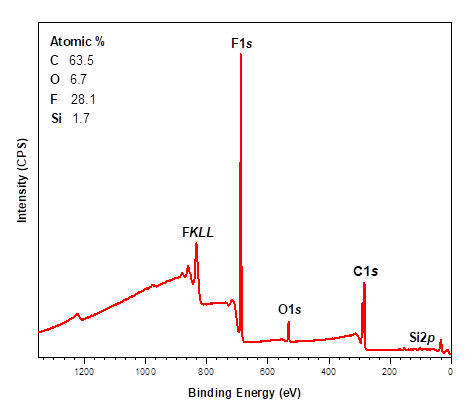
X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) is a highly surface-specific chemical analytical technique used to probe the elemental composition and...