X-ray imaging, also called Transmission X-ray Radiography or X-ray Computed Tomography is commonly used in many fields to non-destructively visualize internal structures that may be difficult or impossible to see using other imaging methods.
Contact Us to learn how this technique can be used to resolve your metrology questions.
Advantages of X-ray Imaging
- X-ray imaging is non-contact and non-destructive.
- X-ray imaging illuminates subsurface and internal structures and features within devices.
- X-ray imaging can produce 2D, 2.5D and 3D reconstructed images and renders.
- X-ray imaging is a well-understood technique with developed methods for a variety of industry applications.
Application Areas
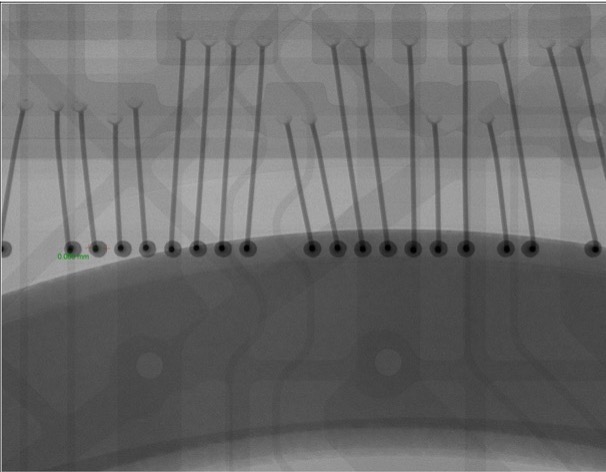
Electronic circuit inspection: X-ray imaging is commonly used in the electronics industry to inspect the internal structure of electronic devices, such as printed circuit boards (PCBs), integrated circuits (ICs), and microelectromechanical systems (MEMS). This allows for non-destructive testing of the devices to identify defects, such as voids, cracks, and delaminations.
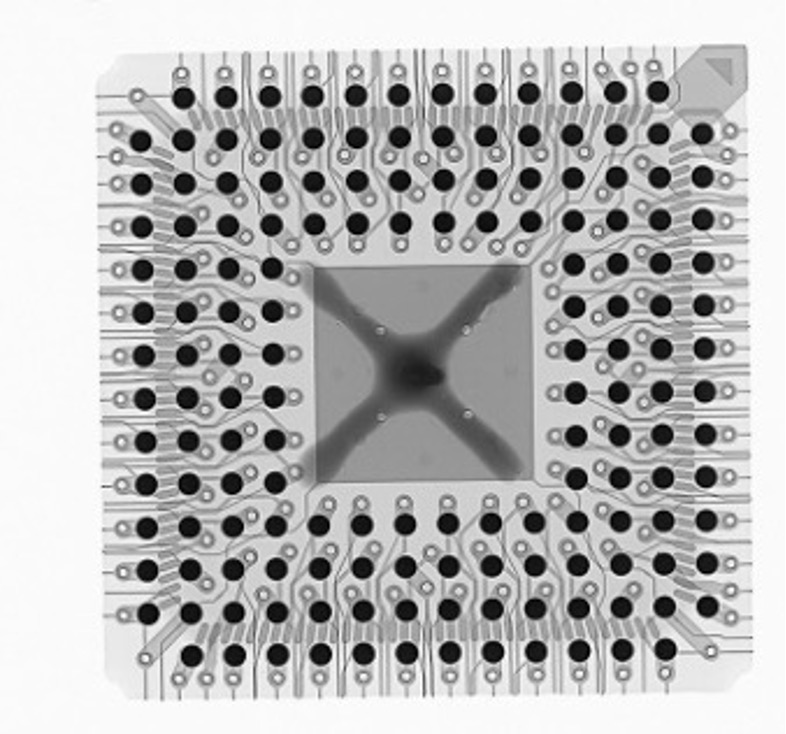

Failure analysis: X-ray imaging is also used for failure analysis of electronic components, especially ICs. This may involve identifying defects in the packaging, such as delamination or cracking, or examining the internal structure to identify faults such as bridging, opens, or shorts.
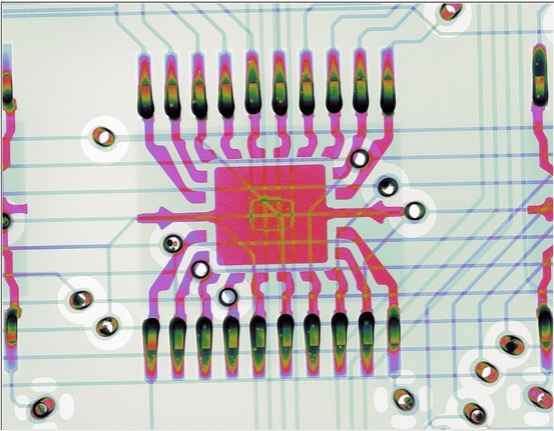
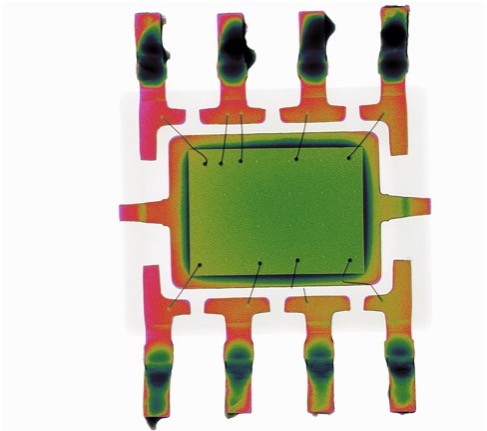

Counterfeit detection: X-ray imaging is used to detect counterfeit electronic components. Genuine components have a unique internal structure, which can be compared to reference images to identify fakes that have been re-labeled or re-packaged.
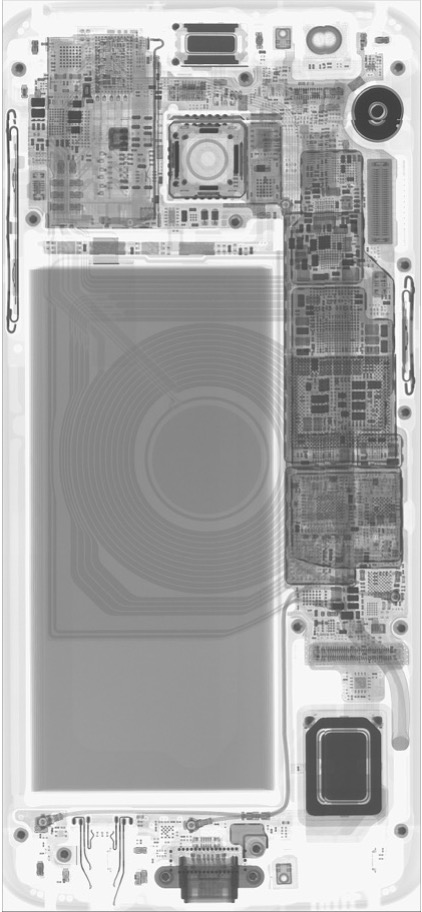

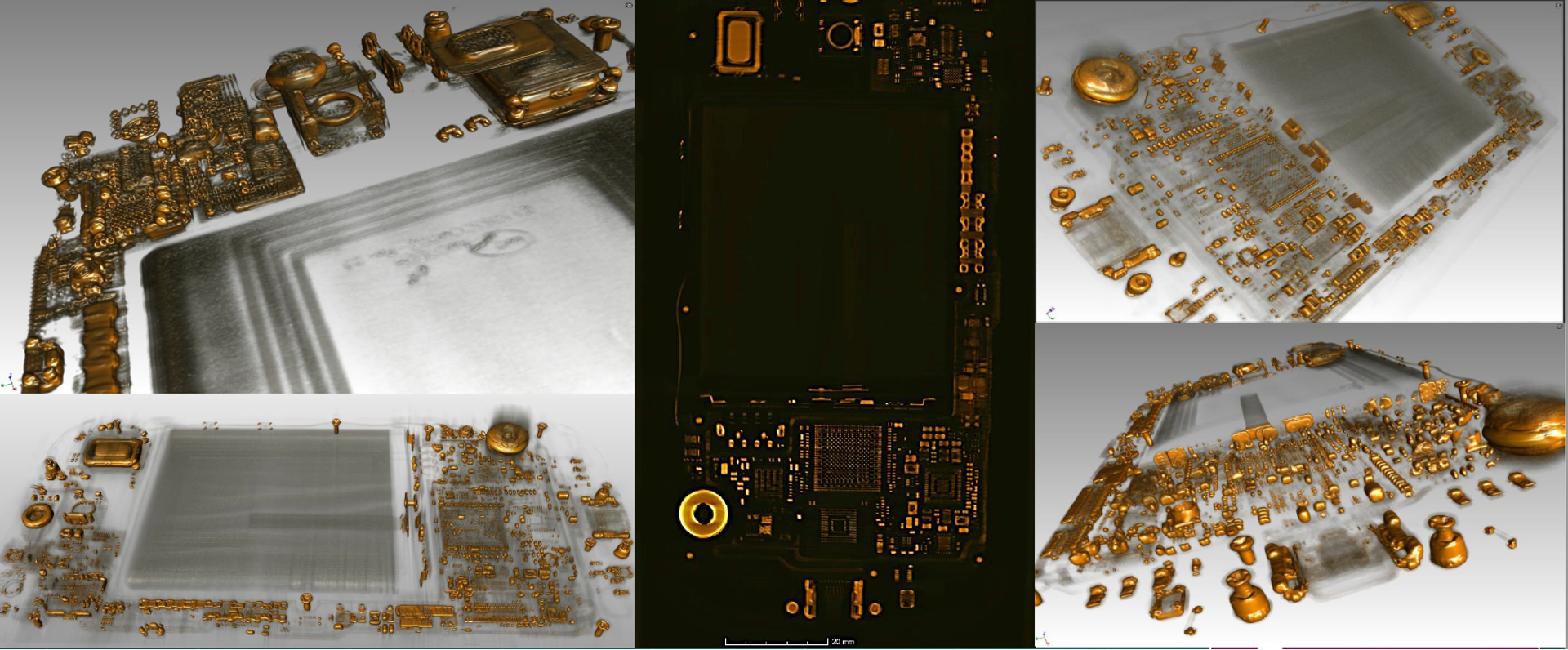
IP infringement: X-ray imaging can be used to analyze electronic devices by creating 3D models of their internal structure. This is useful for analyzing the design of a competitor’s product or for identifying IP infringement.
Industrial inspection: defects and quality control of manufactured parts, welds, and pipes.
Aerospace and automotive engineering: non-destructive inspection of critical components such as turbine blades, engines, and other parts of aircraft and automobiles for quality assurance and safety purposes.
Archaeology and art conservation: visualize buried or subsurface features of historical artifacts and artwork without damaging the piece.
Let’s chat about how X-ray Imaging can illuminate solutions for your materials and devices.

