Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR)
$99 Base price View My Quote RequestNanomechanical Scratch Test (Nano-Scratch)
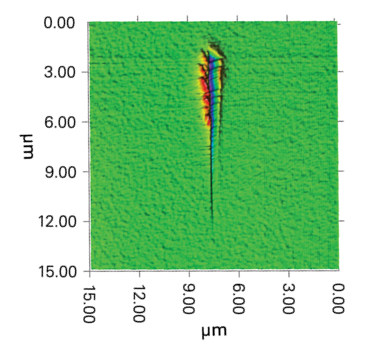
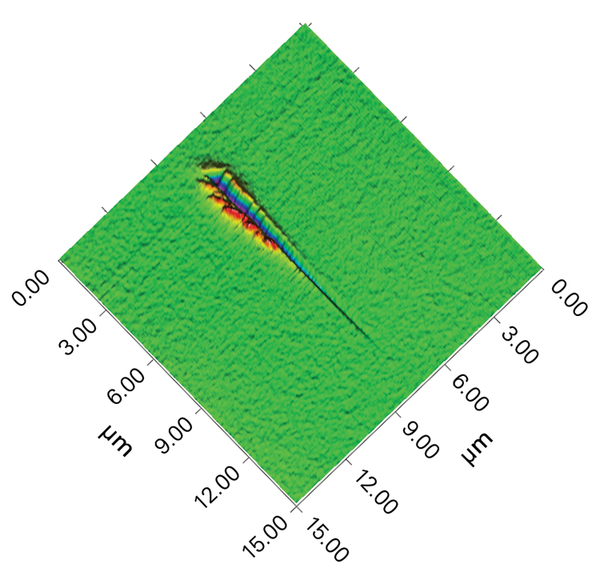
Nanomechanical scratch testing (nano-scratch) is an alternate nanomechanical testing mode to nano-indent or nano-wear box testing, which is used to measure force response and mechanical properties typically of thin films and coatings.
- Works on thin films (10nm and more)
- Advanced mechanical analysis of nano- or micro-scale solids
- Optimized toughness / adhesion test for thin films 10 nm or thicker
- Efficient data collection
- Minimal sample preparation
- Destructive
- Not well suited to measure ultrathin layers (less than 10 nm)
- Interpretation is challenging if films are less than 100 nm and/or surface is rough
Technical Specifications:
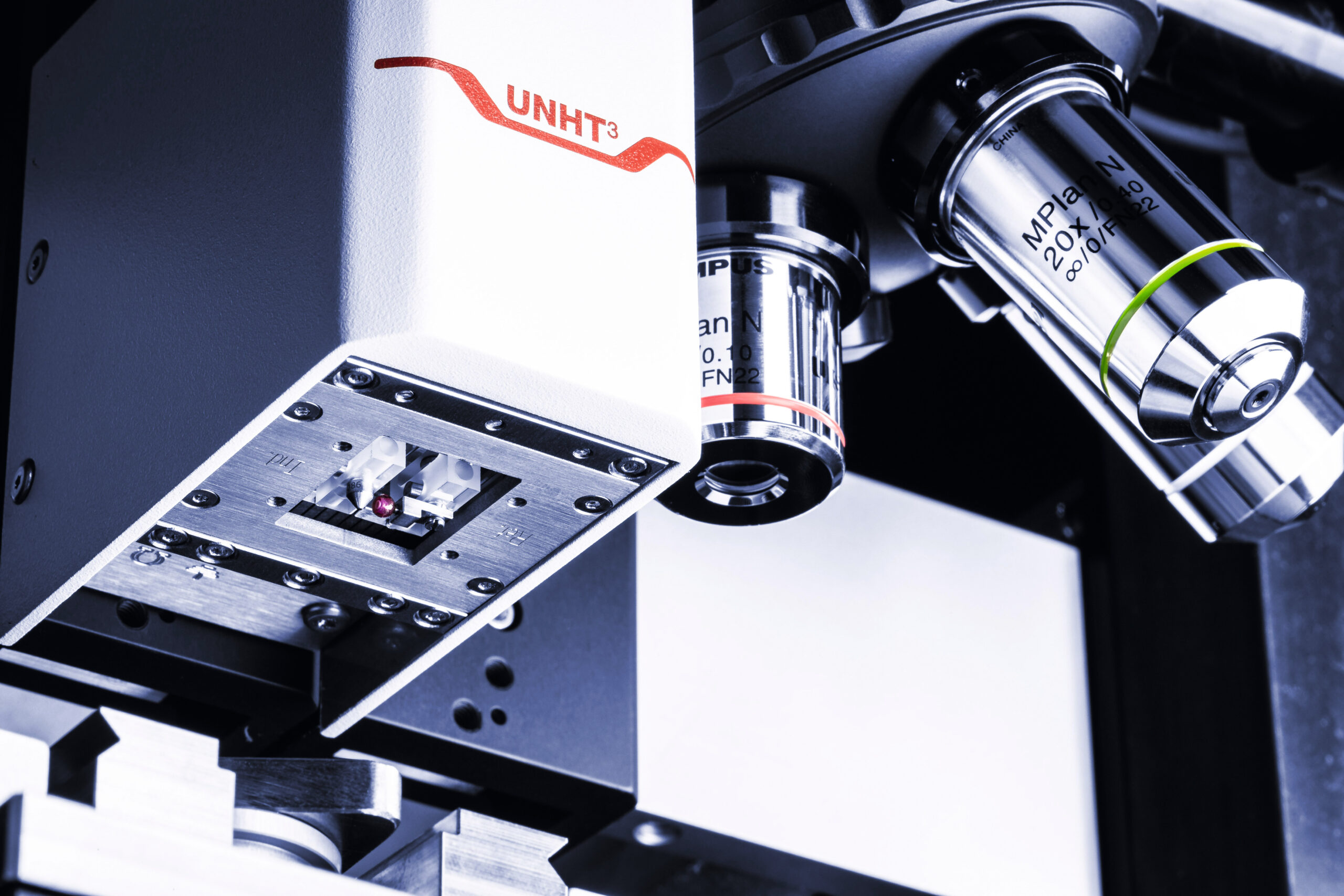

Anton Paar STeP 6 Platform
- Multiple Nanomechanical Testing Heads:
- UNHT3: Ultra Nanoindentation Tester
Normal Load Range: 10 μN to 100 mN - NST3: Nano-scratch Tester
Normal Load Range: 10 mN to 1 N
- UNHT3: Ultra Nanoindentation Tester
- Depth Range: 10 nm to 100 μm
- Acoustic enclosure with anti-vibration table
- Heated stage
- Integrated optical video microscopes for synchronized panoramic imaging during force measurement
- Long-term thermal stability for elevated-temperature analysis
In nano-scratch testing, both thin films and bulk solids can be characterized, and a more diverse array of deformation and fracture features can be analyzed as compared to standard nano-indentation.
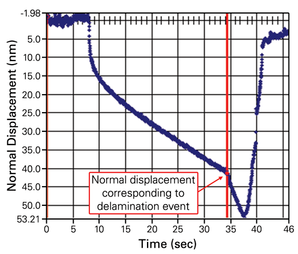
In this measurement mode, a calibrated force normal to the sample surface is applied to an indenter tip while it is skimmed across the sample. In addition to standard penetration depth and indent characteristics, the nano-scratch test also calibrates and measures the amount of force required to keep the tip moving laterally across the sample surface.
The tip force, displacement, and optically profiled sample damage are then jointly analyzed to interpolate nanomechanical properties of the specimen, including: friction co-efficent, adhesion, hardness, and more.
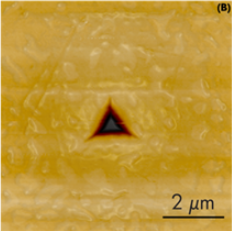
Nanoindentation (Nano-Indent)
Nanoindentation is a quasi-static mode of nanomechanical analysis used to measure hardness and reduced elastic modulus of solid...