Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR)
$99 Base price View My Quote RequestLaser Scanning Confocal Microscopy (LSCM)

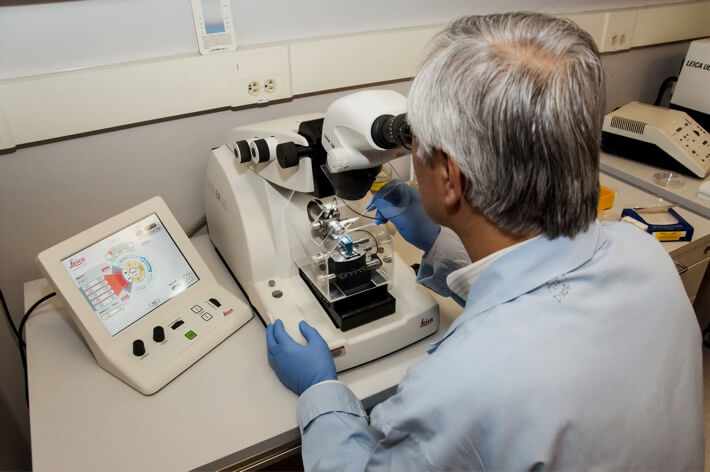
Laser scanning confocal microscopy (also called “VK” for the instrument used) is a nondestructive technique which generates 2D and 3D images of a sample surface.
Covalent’s laser confocal microscopes can accomplish both optical imaging (using broadband white light) and laser-confocal imaging.
- Controlled depth-of-field
- 3D reconstructions and visualizations are possible with serial sectioning
- Straightforward, relatively rapid data collection
- Optical properties of material determine end data quality
- High-energy laser source can cause damage to live cells and tissues
Technical Specifications:
Learn More:
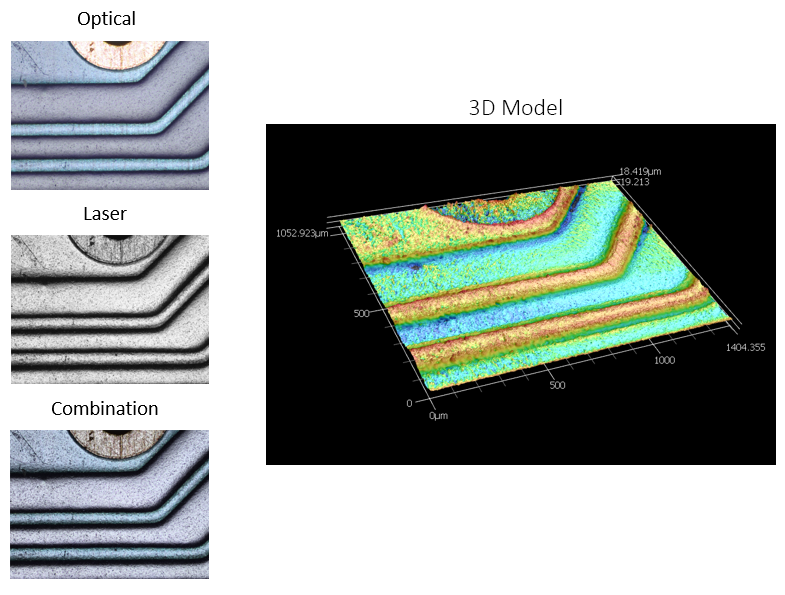
Images captured from the white light source (optical) and laser, as well as the combined image showing how the system captures highly accurate depth contrast as well as the true color of the different pieces of the sample. Pictured at left is a 3D model generated from the height profile of the sample surface; in this image, contrast and color is keyed to height instead of true sample color
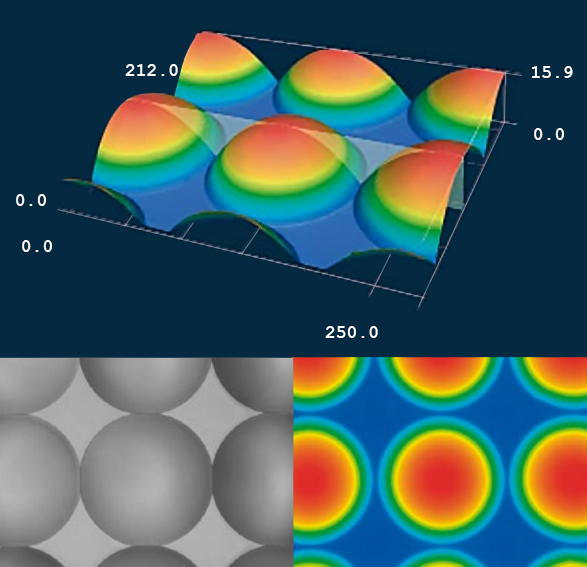
3D models generated from LSCM scans of microlenses, showing radius and circularity
From: Keyence
- Typically solid phase
- Standard Set-up:
- Lateral Dimension Limit: 200 mm x 200 mm
- Vertical Height Limit: 100 mm
- Samples may be either conductive or insulating
- Nonstandard topologies and larger samples can be accommodated creatively.
Please contact us to discuss larger-sample LSCM analysis options
For Laser-Confocal Microscopy, a laser source beam is passed through a set of optics which include narrow pinholes. The effect of these pinholes is to provide a very shallow depth of field such that only light which is reflected from near the exact focal plane of the final lens will reach the detector.
The microscope captures a series of vertical slices (in z-dimension) to build up a 3-dimensional profile at the illuminated beam spot. By scanning this spot in a raster-pattern laterally (in x-y plane), the system generates an image profile of the sample surface topography.
Nanometer-scale resolution can be achieved, depending on the focusing lens used for the measurement.

Optical Microscopy and Profilometry Services

Datasheet: Medical Device Characterization with the Covalent Platform

Overview: Mid-Range Optical Profilometry
Datasheet: Covalent Keyence Instrument Overview

Choosing the Right Surface Imaging Technique
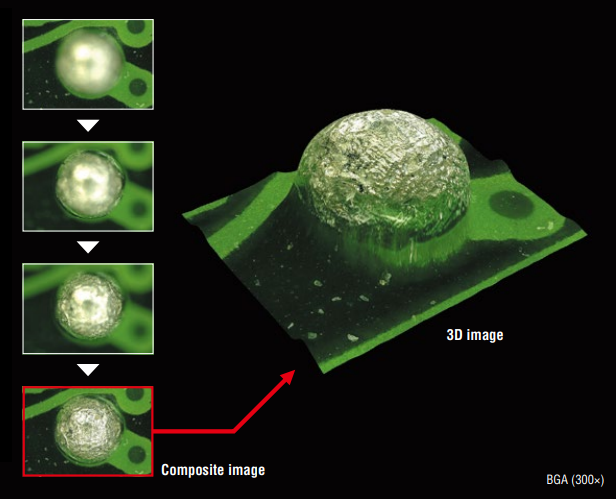
Digital Optical Microscopy (VH Microscope)
Optical microscopy is ubiquitous in diverse fields within academic research and commercial industries. It is an affordable, rapid...
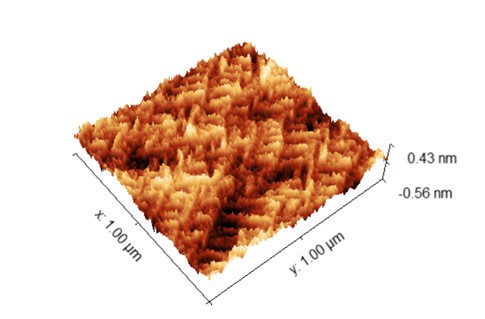
Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
AFM measures surface topography and certain material properties with sub-nm vertical resolution and atomic-level force sensitivity.
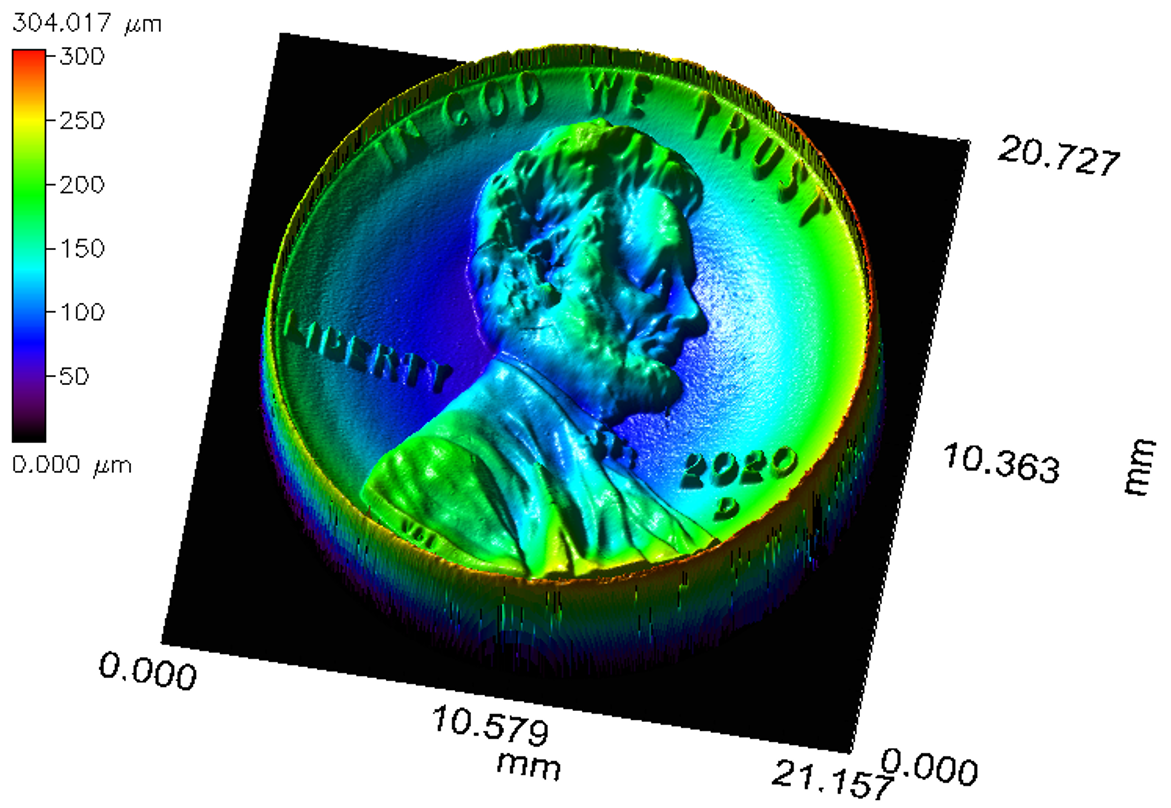
Chromatic Dispersion Profilometry (CWL)
Chromatic dispersion profilometry is a non-contact, nondestructive analytical technique used to measure surface topography. It is particularly well...

Laser Scanning Confocal Microscopy (LSCM)
Laser scanning confocal microscopy (LSCM) is a nondestructive technique which generates 2D and 3D images of a sample...
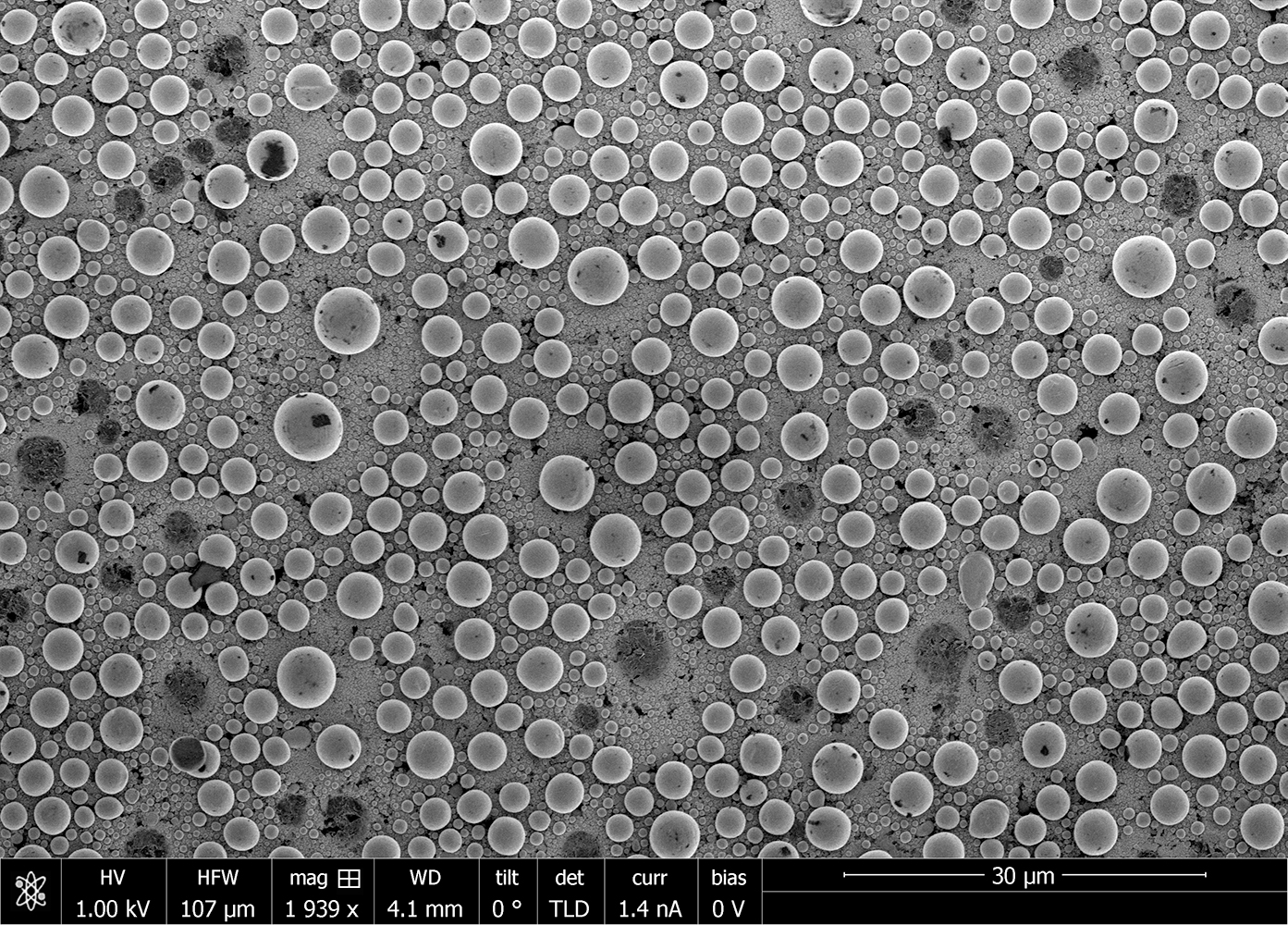

Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) is a surface imaging technique capable of achieving nm resolution on topographical features. Additionally,...
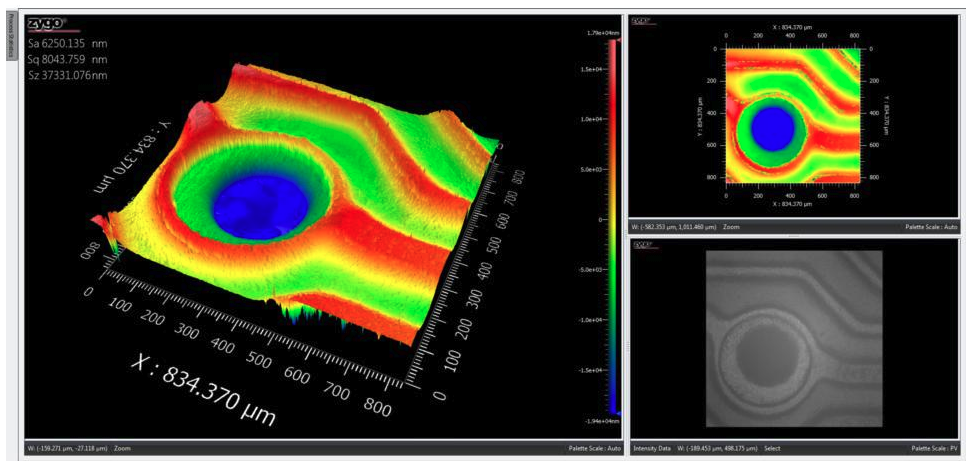
White Light Interferometry (WLI)
White light interferometry (WLI) is a nondestructive, non-contact, optical surface topography measurement which uses coherence scanning interferometry to...
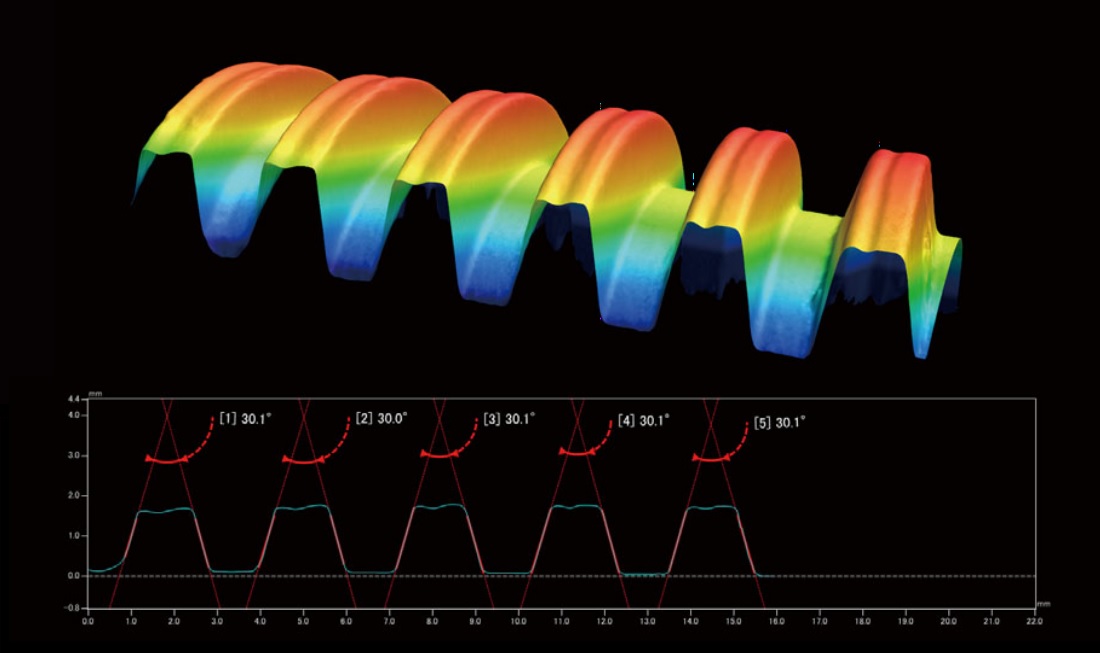
Wide Area 3D Patterned Light Measurement (VR)
Wide Area 3D Patterned Light measurements encompass a class of optical profilometry techniques used to visualize the surface...



