
Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR)
$99 Base price View My Quote RequestUltraviolet Photoelectron Spectroscopy (UPS)
Ultraviolet photoelectron spectroscopy (UPS) is often performed in conjunction with X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS), a powerful surface chemical characterization technique.
Unique to UPS, its selective low-energy signal photoelectrons enables specific measurement of valence-band properties, as well as the electronic work function of the surface.
- Very high surface specificity: information depth 2-4 nm
- Highly accurate spectral fingerprinting
- Selective valence-band signal: bonding orbital properties
- Reliable work function measurements possible
- UPS peaks are not used for elemental quantification: degree of hybridization and extent of BE-shift is too substantial
- Robust density of electronic states / orbital occupancy typically requires Advanced Modeling
- Work function measurement requires careful setup to isolate sample low-KE cutoff from detector behavior
Technical Specifications:
Learn More:

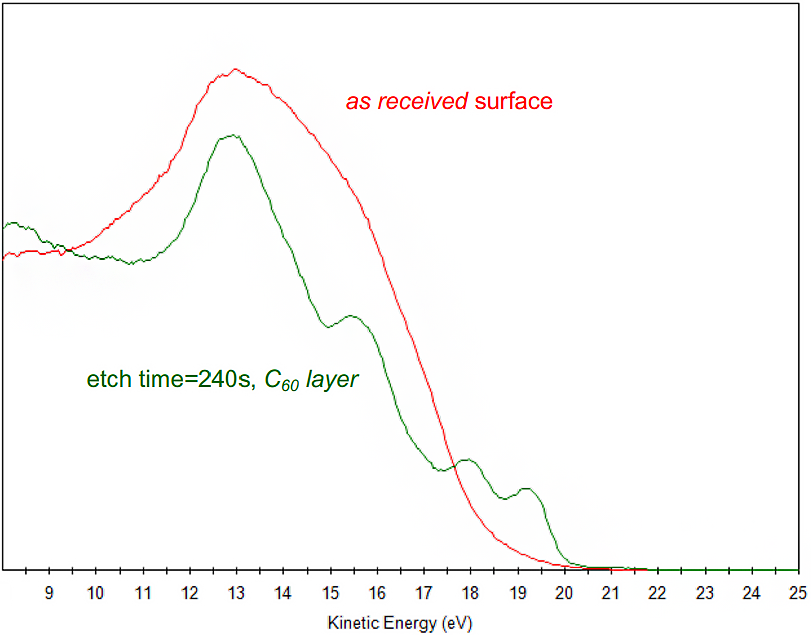
He(I) UPS spectra from 10 nm fullerene (C60) film on CaF2 substrate before any surface cleaning (by ion cluster etch), and after initial surface cleaning. As received, the sample showed overlaying amorphous carbon contamination that obscured measurement of the C60 film.

He(I) UPS spectra from 10 nm fullerene (C60) film on CaF2 substrate at 2 more etch times. After 900 second etch, the valence electron structure has shifted away from the C60 bonding configuration (shown above).
In UPS measurements, a high-energy laser beam is applied to the sample surface, and characteristic photoelectrons are emitted via the photoelectric effect. The emitted photoelectrons are then analyzed by energy to produce a spectrum of peaks associated with the quantitative concentration of specific elemental species.
Unlike XPS, UPS uses an ultraviolet-laser source, which limits the amount of energy imparted to the surface atoms.
As a result, UV photoelectrons are selectively emitted from outer (valence-band) orbitals, and the information depth is more surface specific. These features enable more detailed analysis of the valence-band properties and bonding states and provide a direct measurement of work function.
The ability to clean the surface using Argon ion clusters ensures that work function measurements can be done with clean rather than environmentally contaminated surfaces.

E-Book: Surface Spectroscopic Techniques for Chemical Analysis
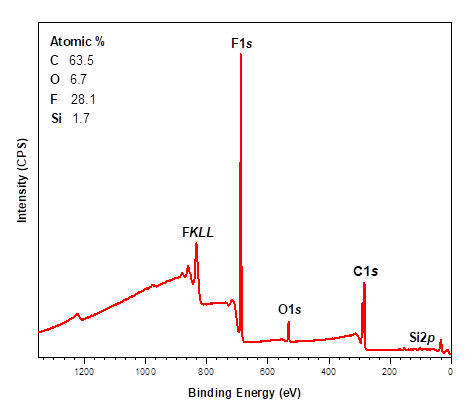
X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) is a highly surface-specific chemical analytical technique used to probe the elemental composition and...
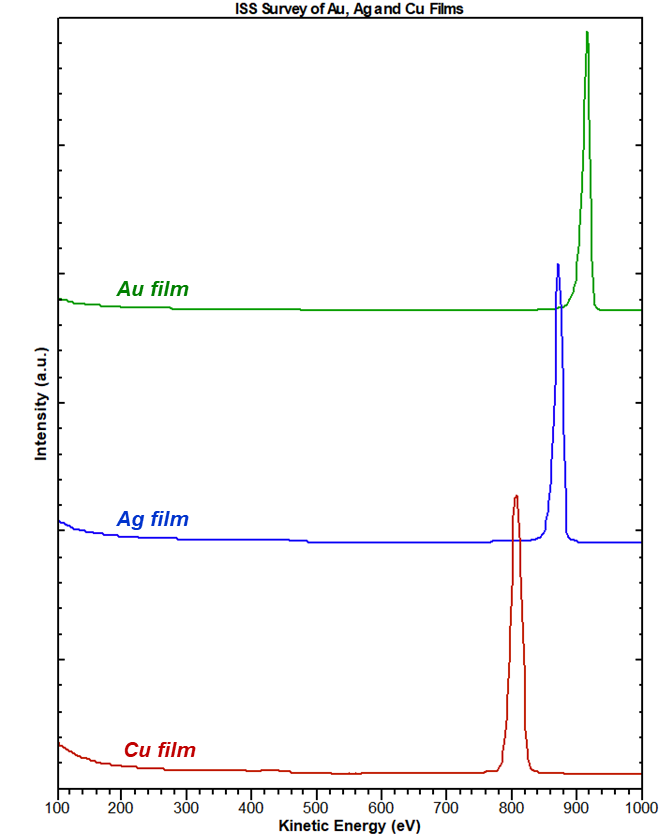
Ion Scattering Spectroscopy (ISS)
Ion scattering spectroscopy (ISS) provides quantitative elemental composition information from the very outermost atomic layer of a surface....
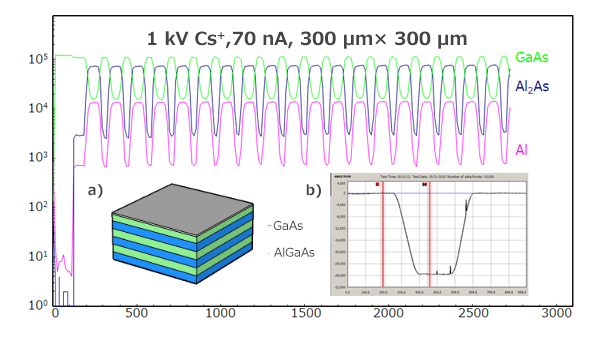
Time of Flight Secondary Ion Mass Spectroscopy (ToF-SIMS)
Time of flight secondary ion mass spectroscopy (ToF-SIMS) is a highly surface-specific analytical technique used to qualitatively assess...


