Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR)
$99 Base price View My Quote RequestDynamical Mechanical Analysis (DMA)

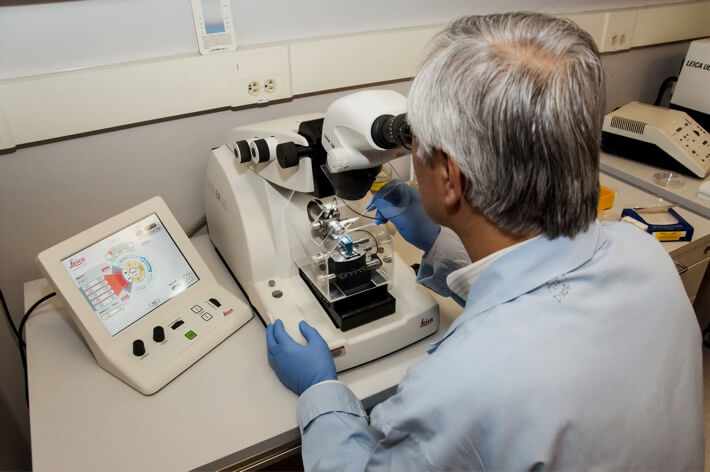
Dynamical mechanical analysis (DMA) is used to study changes in the mechanical properties of a material under periodic stress as the temperature is varied. DMA results are used to assess: glass transitions, melting points, elastic modulus, strain-to-break, toughness, creep, and numerous other thermal and mechanical properties.
- Ultra-high sensitivity to deformation and displacement
- Improved detection threshold for thermal transitions (vs. Differential Scanning Calorimetry)
- High flexibility in experiment design
- Rapid and straightforward data collection
- Particularly well-suited for high-stiffness polymers
- Data quality is impaired by rough, asymmetric, and irregularly-shaped samples
- Analysis is destructive
Technical Specifications:
Learn More:

DMA curves used to measure glass transition temperature (Tg) in CFRP polymeric composites using 3 different metrics: Storage modulus, Loss modulus, and Temperature. Broadening of the range of measured Tg values (as shown in this sample) can be indicative of polymer crosslinking.
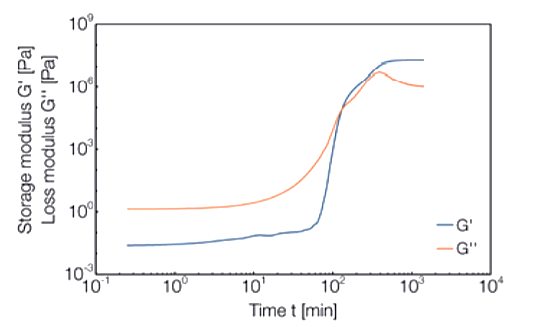
DMA curve of moduli as functions of time. Curve shape is characteristic of epoxy resin material during the cross-linking reaction (G’, G” cross-over).
In a DMA measurement, an oscillating force is applied with a set frequency to a sample suspended in a near-frictionless environment. This force can be set to bend, stretch and compress, torque, or maintain tension directionally within the sample.
While the dynamic stress is applied to the sample, the whole system is simultaneously subjected to set temperature change: either constant or iterated heating / cooling at fixed or variable rates. The material’s stress response over time is measured both through its dimensional changes and its damping of the oscillating force.
DMA systems detect dimensional changes with hypersensitive optical sensors, and track damping through the applied force probe. These two metrics, recorded as a function of time and temperature, are used to produce DMA curves which provide robust, quantitative analysis of the sample’s thermomechanical characteristics.

4 Targets for Optimization in a Battery Cell
Thermal Solutions: Characterization of Epoxy Reinforced Glass by...

Application Note: Applications of indentation on polymers
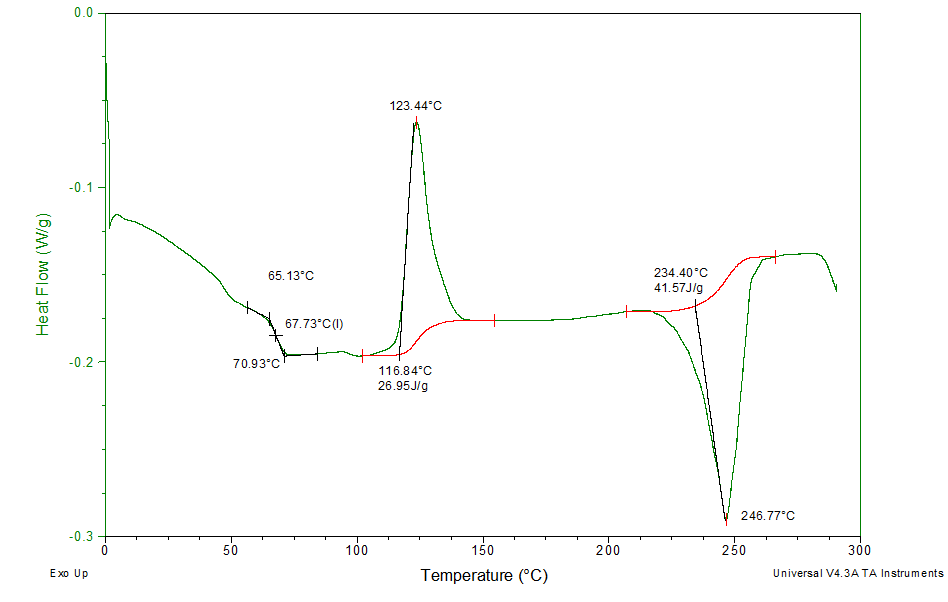
Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
DSC is a thermal analysis technique used to characterize a variety of temperature-dependent physical and chemical changes in...
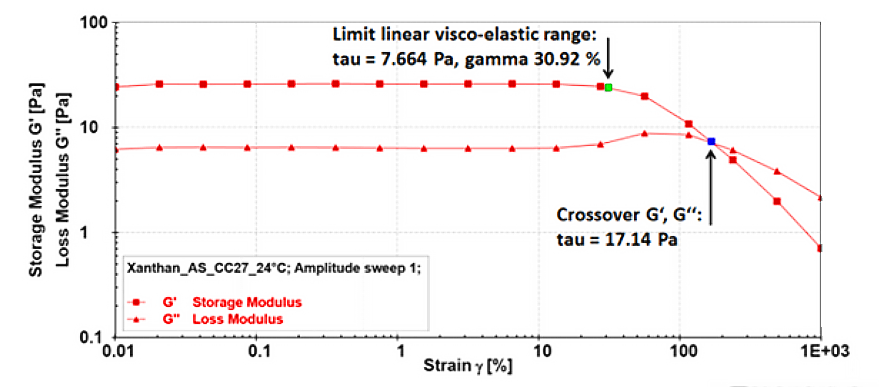
Rheometry (Rheology)
Rheometry measures the flow and deformation of materials in response to applied stress and strain to evaluate their...
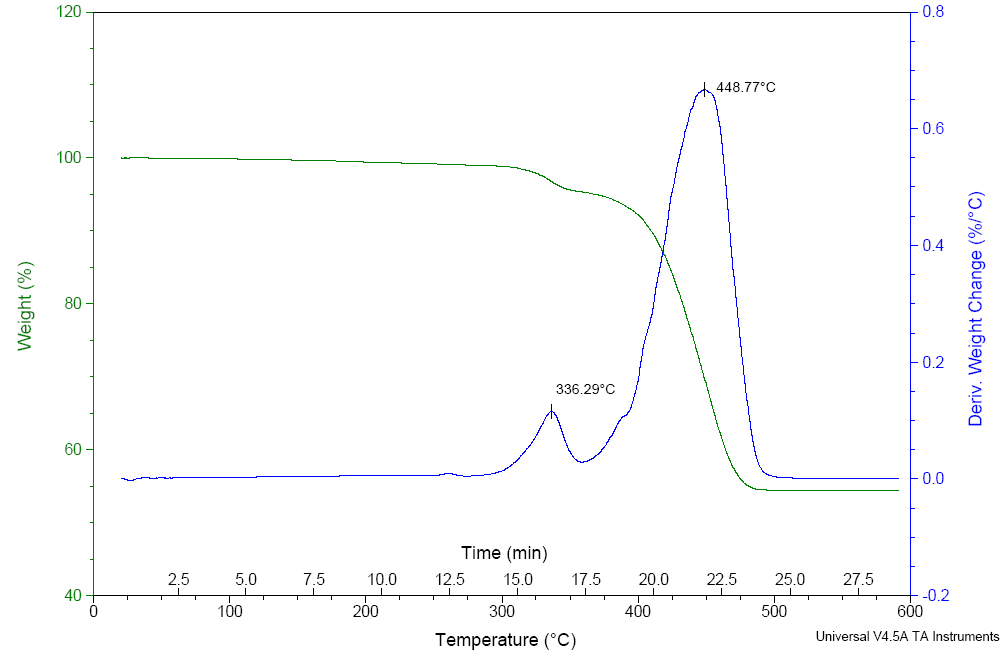
Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) is used to characterize sample volatility, as well as thermal stability and response. TGA instruments...
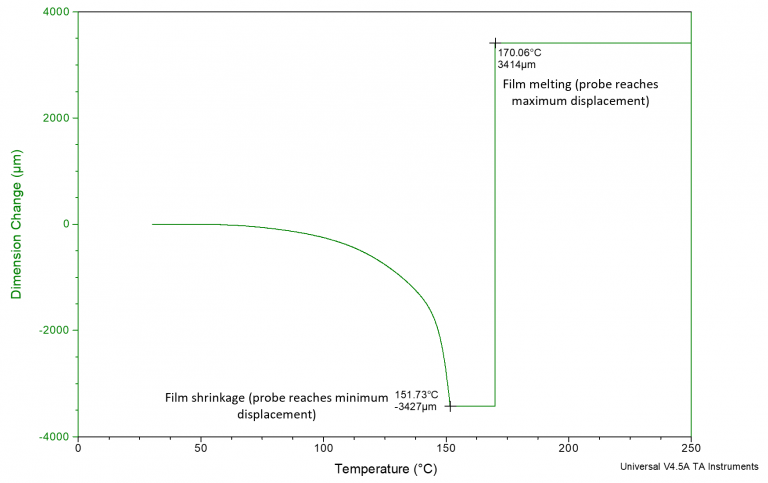
Thermomechanical Analysis (TMA)
Thermomechanical analysis (TMA) probes the response of the sample’s thermal, dynamic, and static-mechanical properties as temperature is changed...


