Particle Analysis

Covalent provides direct and indirect particle size analysis, as well as particle zeta potential measurement to characterize the electrokinetic potential of colloidal dispersions.
Particles play a role in many industries: pharmaceuticals, slurries, polishes, powders, and industrial abrasives; they are even used in quantum dots and battery electrodes. In all these applications, particle analysis supplies key quantitative and qualitative information about the overall particle size distribution and even particle morphology.
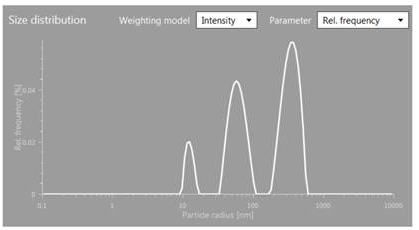
Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
Dynamic light scattering (DLS) is an indirect, high-throughput method for measuring the sizes - by hydrodynamic diameter (HDD) - of particles in a solution.
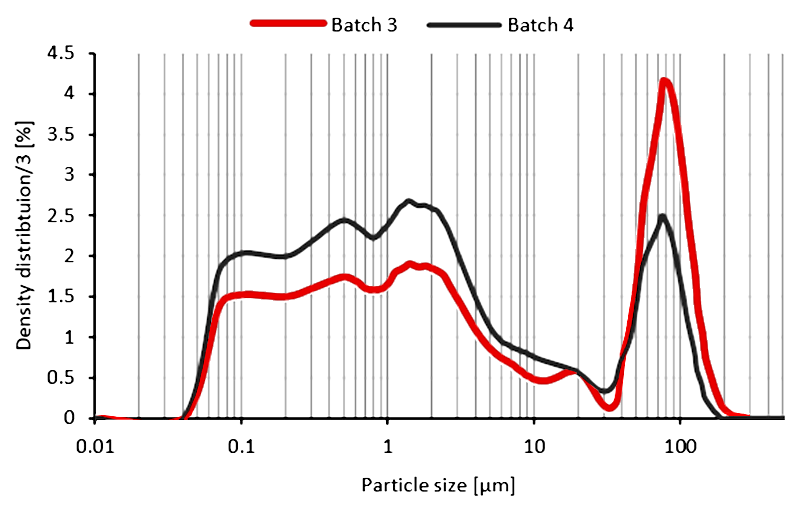
Laser Diffraction Particle Size Analysis (PSA)
Particle size analysis (PSA) is an indirect, optical technique used to measure particle size distributions - by equivalent spherical diameter (D10, D50, D90) - in liquid and solid samples.

Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy (STEM)
Scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM) is a hybrid electron microscopy technique used for imaging and morphological characterization with atomic-scale resolution. STEM is available on both Covalent's FIB-SEM instruments, as well as our TEM. All Covalent's (S)TEM systems are additionally equipped with fully integrated energy-dispersive x-ray spectrometers (EDS or EDX) to allow correlative elemental composition and mapping analysis.
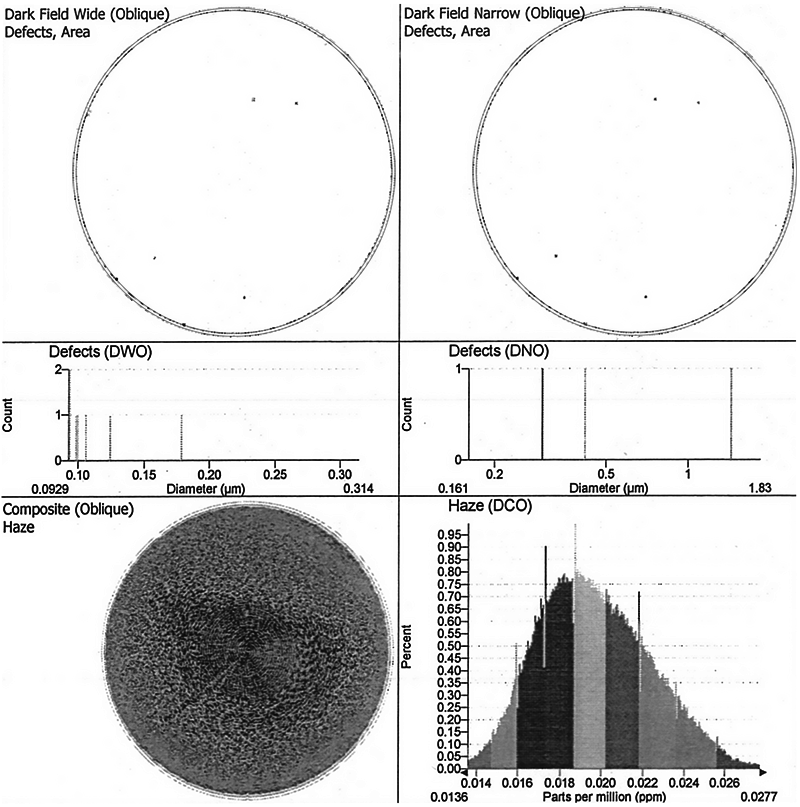
Surfscan® Particle Counting (Surfscan)
Particle counting by Surfscan® (“Surfscan”) is an optical, non-contact surface characterization technique designed to accomplish rapid detection of particles and in some cases wafer defects. It is one of the most common ways to quantify the number and size of particles dispersed across the surface of an unpatterned wafer (often called a blanket or monitor wafer).
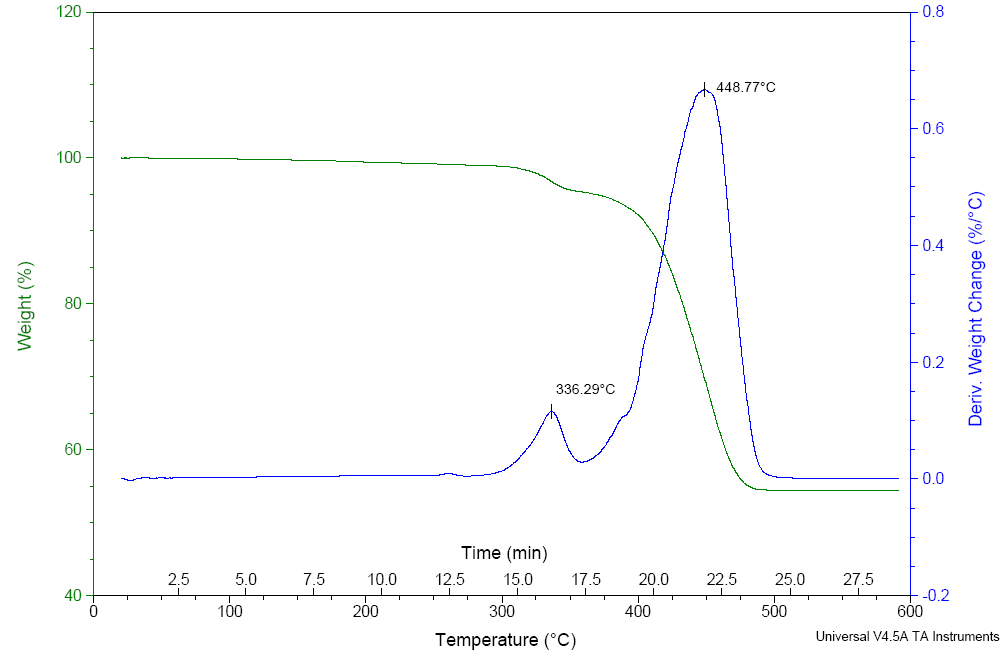
Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) is used to characterize sample volatility, as well as thermal stability and response.
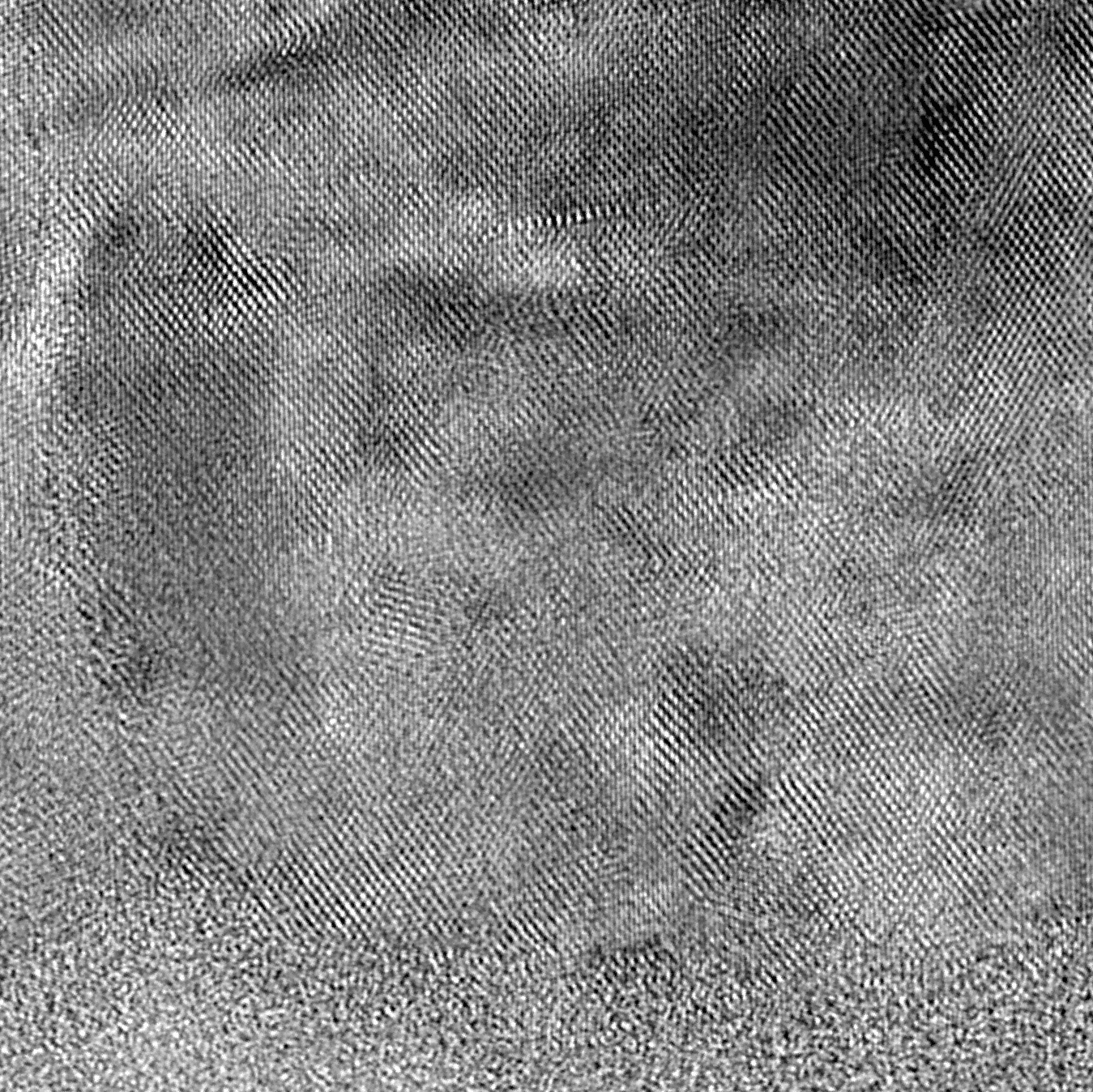
Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) is the highest-resolution imaging technique available today. It is used to visualize sample features with atomic-level spatial resolution limits in order to characterize morphology of complex nanostructures. "These are incredible images. Thanks for the preview. It is so satisfying to get definitive answers to our questions!" - Brad Aitchison, Sr. Process Engineer, Redlen Technologies
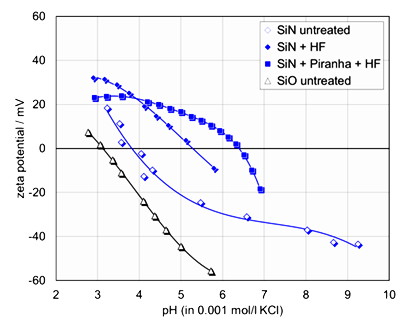
Zeta Potential
Zeta potential measures the strength of net charge on particle and solid surfaces. The higher the magnitude of this potential, the stronger the surface interactions (repulsion and/or attraction) will be when the sample contacts other charged materials.
Techniques Showcase
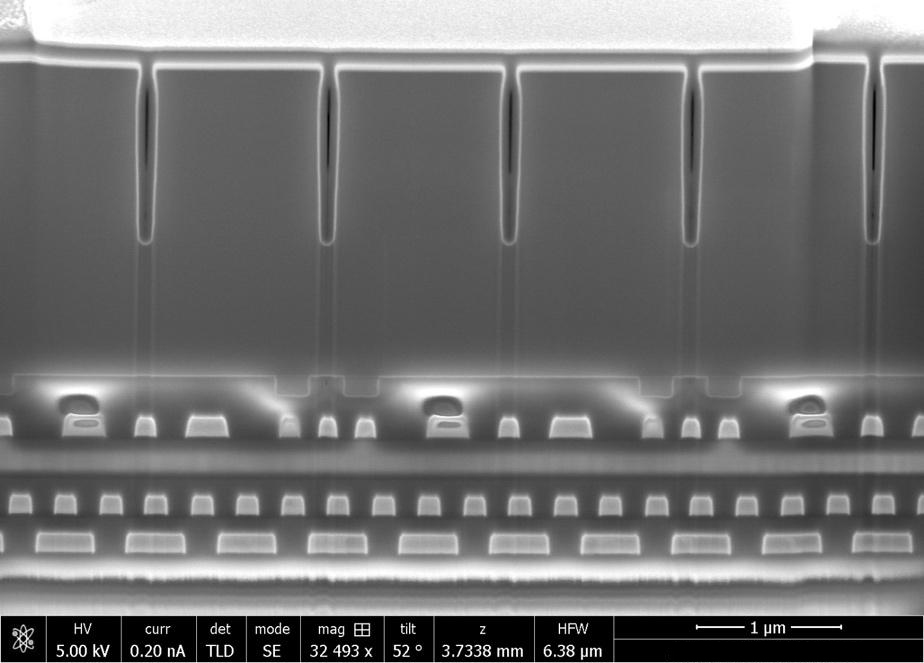
Focused Ion Beam Scanning Electron Microscopy (FIB-SEM)
FIB-SEM systems are used to produce 2D and 3D images of surface topography, and are able to resolve...
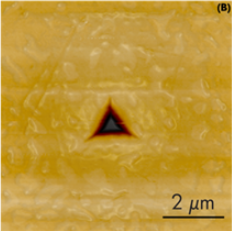
Nanoindentation (Nano-Indent)
Nanoindentation is a quasi-static mode of nanomechanical analysis used to measure hardness and reduced elastic modulus of solid...
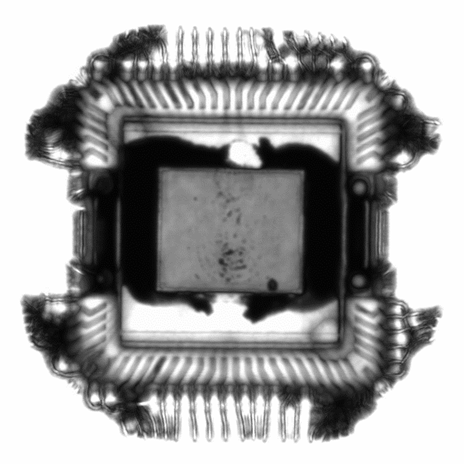
Scanning Acoustic Microscopy (SAM)
Scanning Acoustic Microscopy (SAM) is a non-destructive and non-invasive imaging technique which uses ultrasound signals to visualize the...
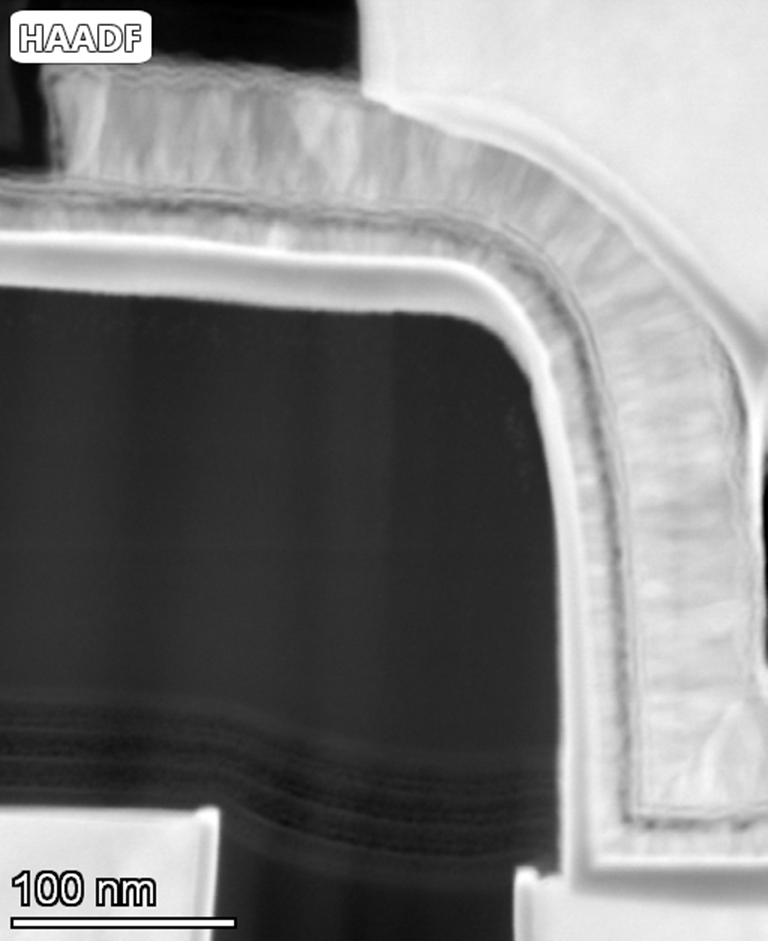

Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy (STEM)
STEM is a hybrid electron microscopy technique used for imaging and morphological characterization with atomic-scale resolution. In Covalent's...
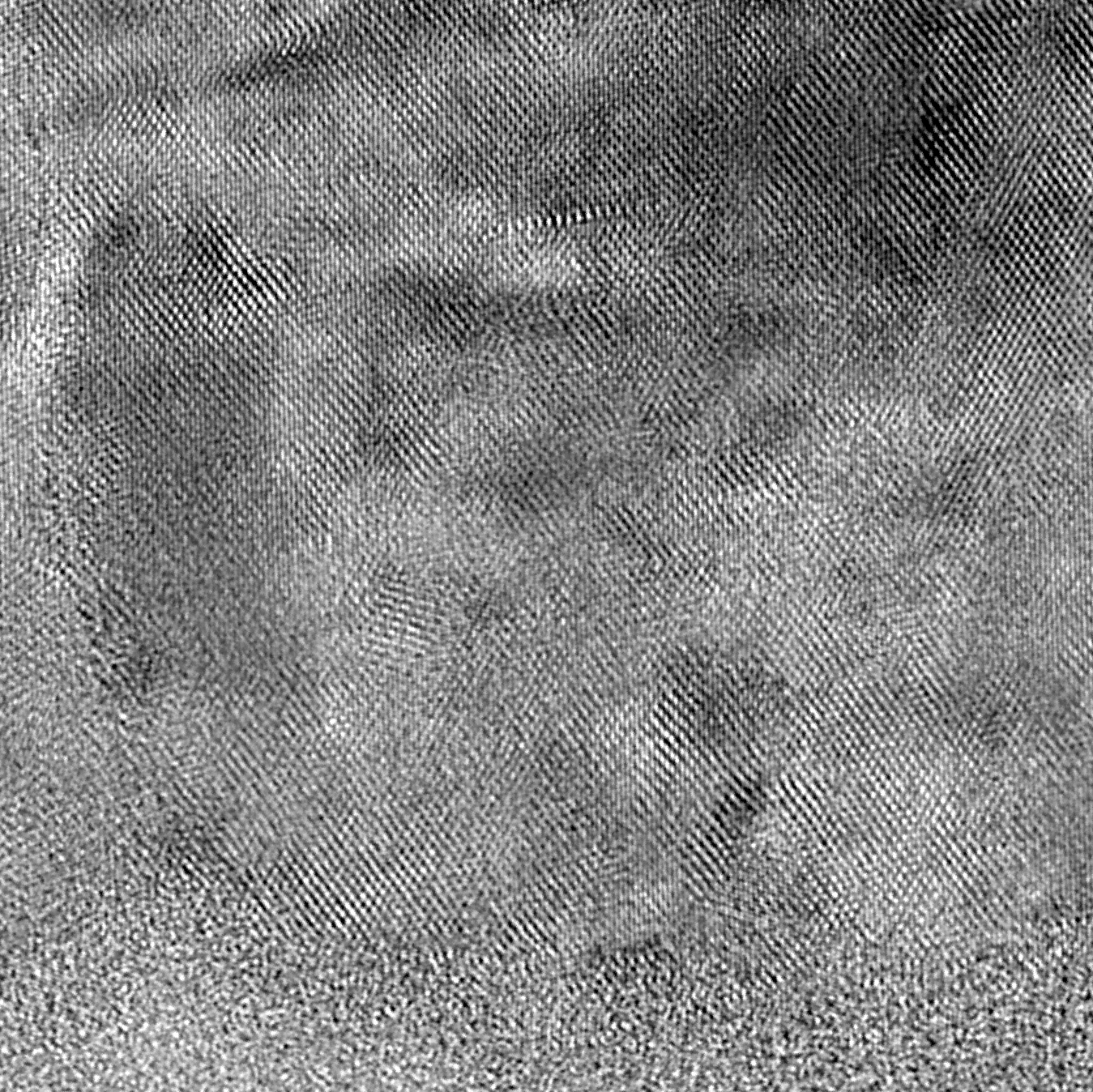
Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
TEM is the highest-resolution imaging technique available today. It is used to visualize sample features with atomic-level spatial...
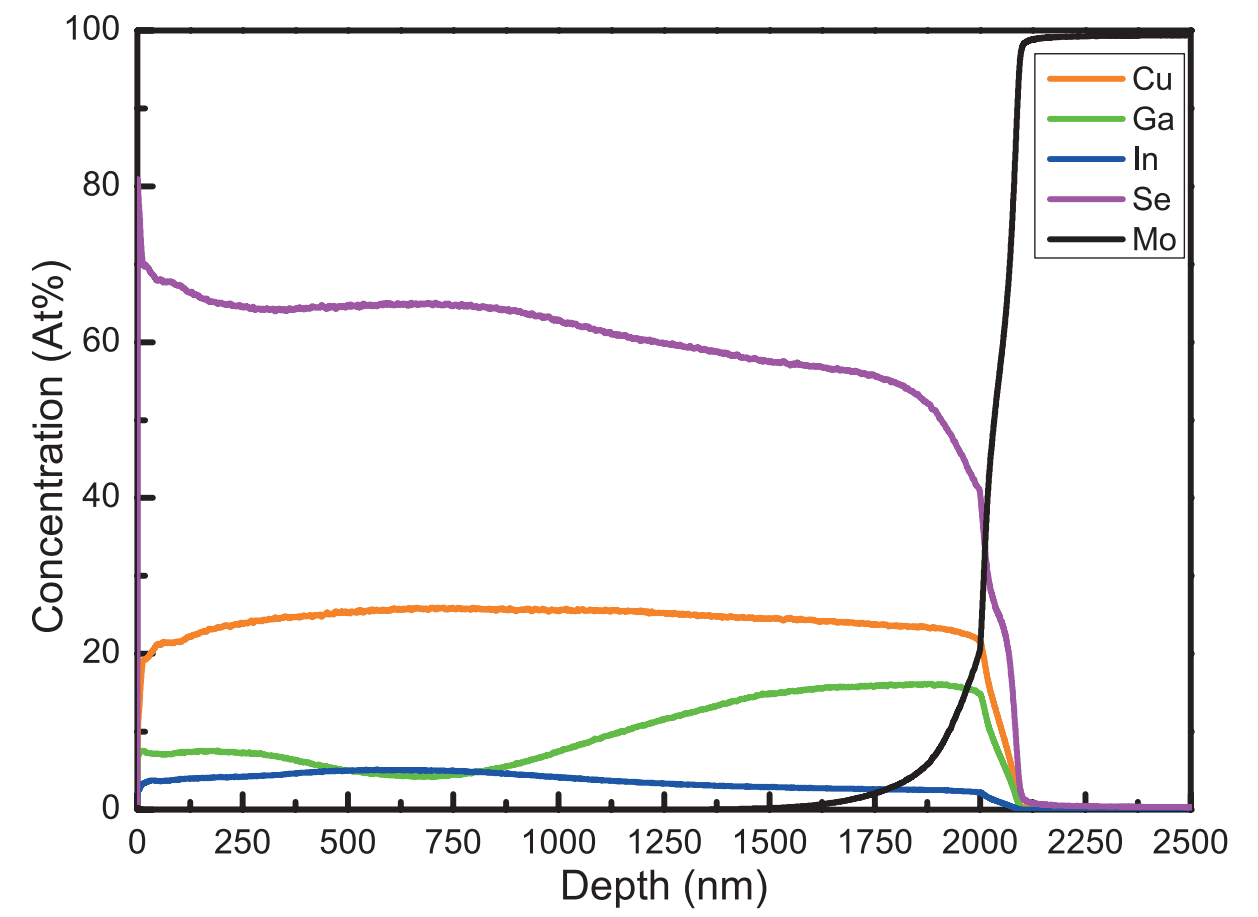
Glow Discharge Optical Emission Spectroscopy (GDOES)
Glow discharge optical emission spectroscopy (GDOES) is a quantitative, chemical analytical technique used to study the elemental composition...

Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectroscopy (ICP-MS)
Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectroscopy (ICP-MS) is a highly sensitive chemical analysis technique which measures the elemental composition...
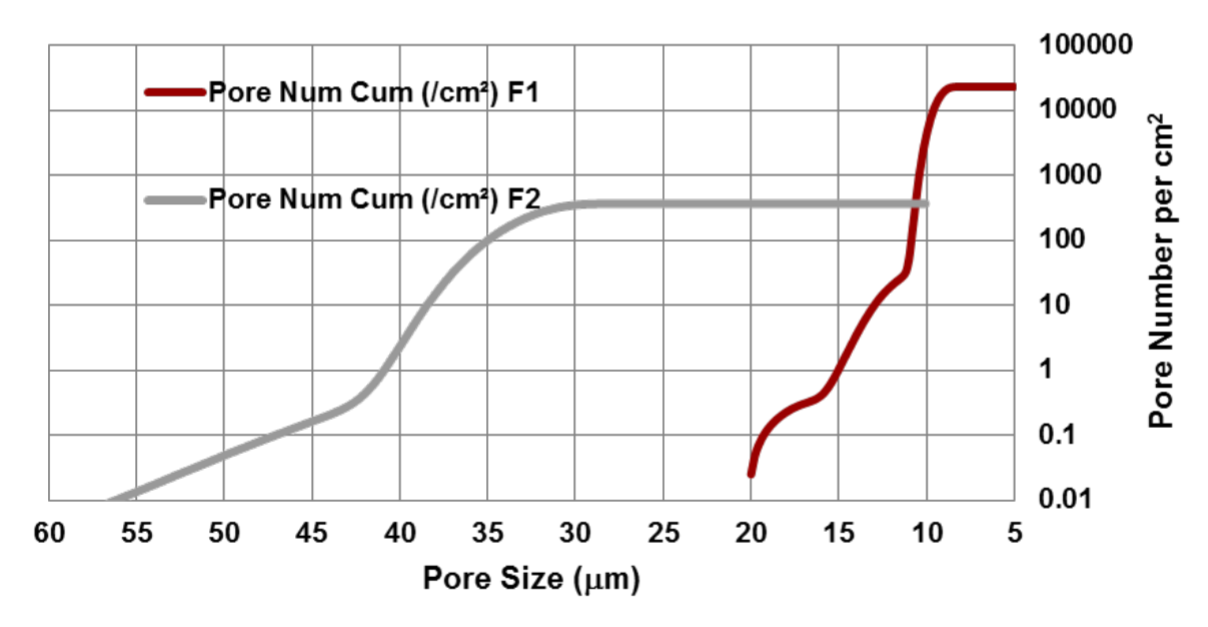
Capillary Flow Porometry (Porometry)
Capillary Flow Porometry (also called Porometry) is an optimal technique for characterizing through-pore size and size distribution.
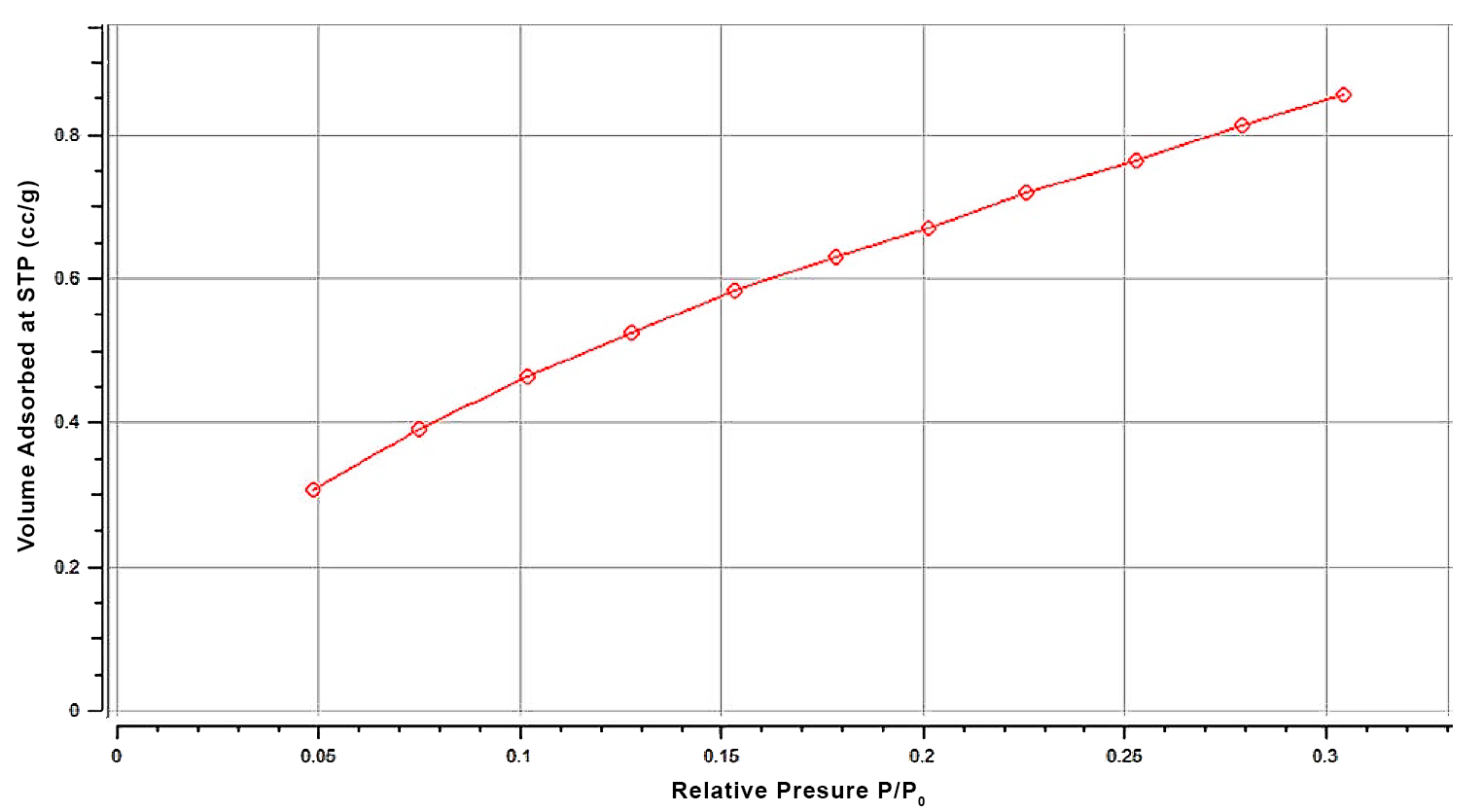
Porosimetry
Gas Adsorption Analysis is used for measuring specific surface area, pore sizes / size distribution, and overall porosity...
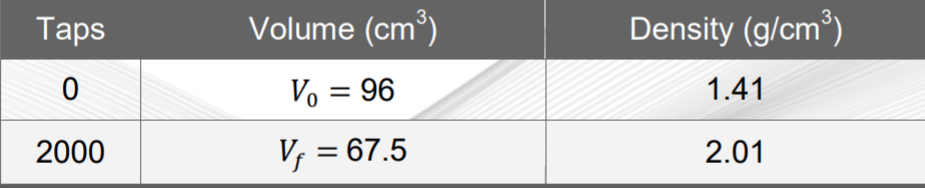
Tap Density Analysis
Tap Density Analysis provides fast, effective measurements of the bulk density of powders and establishes a quantitative metric...

Focused Ion Beam Scanning Electron Microscopy (FIB-SEM)
FIB-SEM systems are used to produce 2D and 3D images of surface topography, and are able to resolve...

X-ray Computed Tomography (Micro-CT)
X-ray computed tomography (often referred to as Micro-CT due to its spatial resolution) is a non-contact, nondestructive 2D...

Nanoindentation (Nano-Indent)
Nanoindentation is a quasi-static mode of nanomechanical analysis used to measure hardness and reduced elastic modulus of solid...


