
Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR)
$99 Base price View My Quote RequestWide Area 3D Patterned Light Measurement (VR)
Wide Area 3D / Patterned Light measurements (VR) encompass a class of optical profilometry techniques used to visualize the surface topography of larger samples.
- Greatest scan area among optical profilometry techniques (cm scale)
- High vertical resolution ( limit < 5 um) with balanced lateral resolution ( ~5 um)
- Non-destructive analysis
- Contour and warp will affect surface roughness analysis
- Highly transparent or specular reflective surfaces
- High aspect ratio dimensions that block the light source
Technical Specifications:
Learn More:

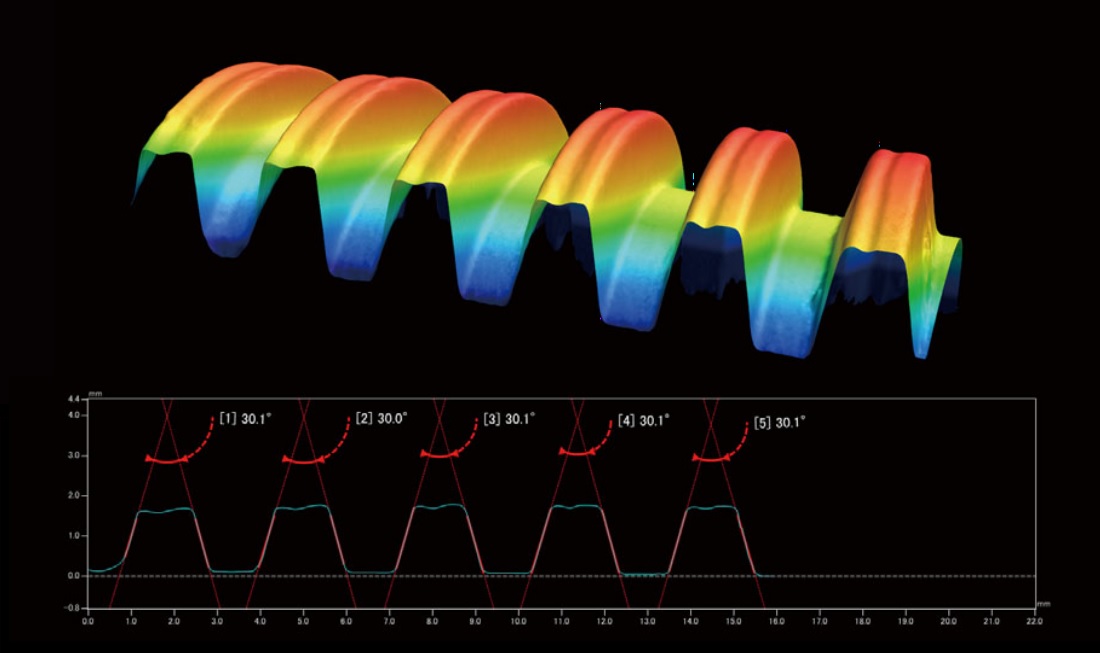
Above shows 3D model output of a trapezoidal screw scanned from single angle; below is a 2D plot showing the critical dimensions of the threads.
From Keyence

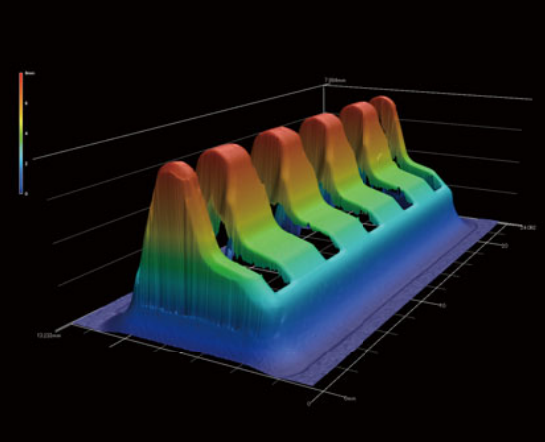
Integrated analysis of 4 different samples, showing: (in leftmost column) top-down true-color images; (in middle column) 3D CAD models generated from the original Patterned Light scans with variable color-coded topographical features – including roughness (A) and total height (C); and (in rightmost column) 2D cross-sectional plots of bump height contrasting the critical dimension of the 4 prongs in each sample.
From Keyence
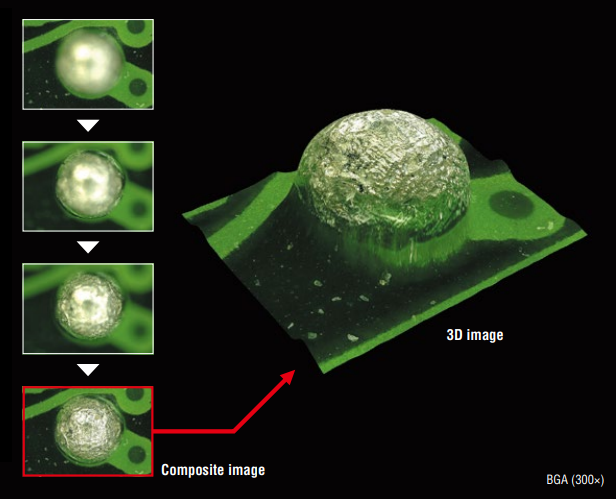
Terminal charge port connector for handheld charging dock.
From Keyence
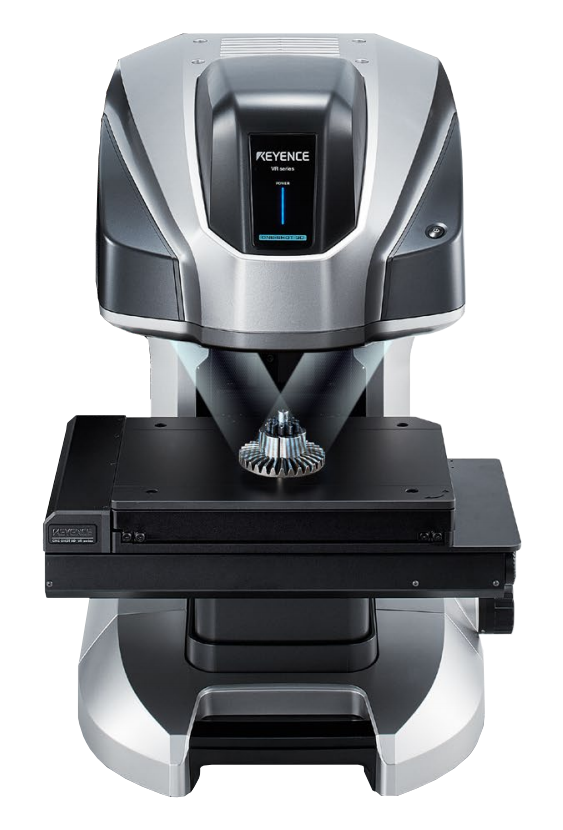

VR-5200
- One-shot 3D Measurements: generate instant 3D CAD model from single scan
- Fully automated stitching of expanded X-Y field of view
- Magnification Range: 12x to 160x
- Maximum Measurable Height Range:
- 10 mm in Wide-Field Mode (magnification up to 50x)
- 1 mm in High-Mag Mode (magnification 40x to 160x)
- Height Accuracy:
- ± 5 μm in Wide-Field Mode
- ± 2 μm in High-Mag Mode
In a Patterned Light measurement, striped patterns of light are projected onto the sample at a known angle of incidence from opposing directions.
A camera mounted directly above the sample captures the distortion of the bands of light due to changes in the height of the samples surface. The measured distortions are triangulated among different patterns to generate a quantitative 3D model of the surface topography.
Unique to this technique, the generated 3D model is compatible for output as a CAD overlay for volumetric comparison in process and part evaluation.

Optical Microscopy and Profilometry Services

Datasheet: Medical Device Characterization with the Covalent Platform

Overview: Mid-Range Optical Profilometry
Datasheet: Covalent Keyence Instrument Overview

Choosing the Right Surface Imaging Technique
Digital Optical Microscopy (VH Microscope)
Optical microscopy is ubiquitous in diverse fields within academic research and commercial industries. It is an affordable, rapid...
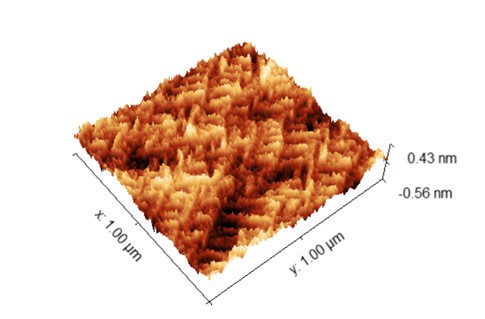
Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
AFM measures surface topography and certain material properties with sub-nm vertical resolution and atomic-level force sensitivity.
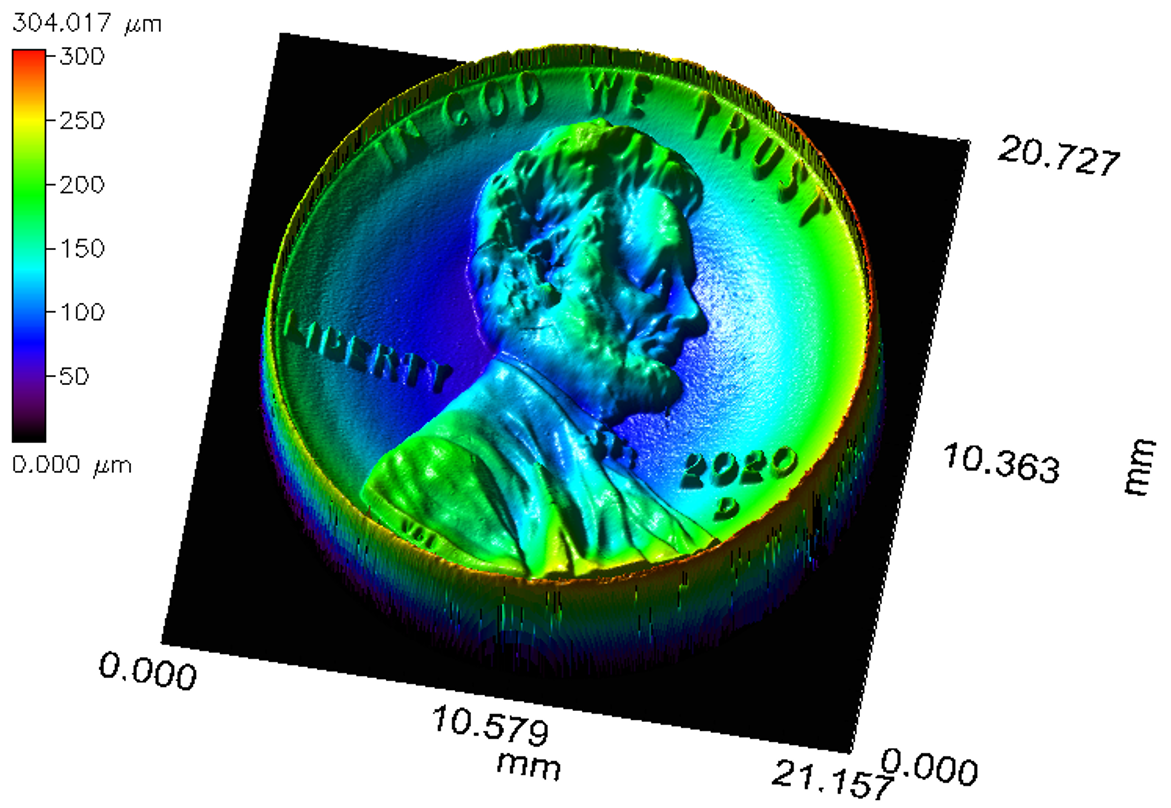
Chromatic Dispersion Profilometry (CWL)
Chromatic dispersion profilometry is a non-contact, nondestructive analytical technique used to measure surface topography. It is particularly well...
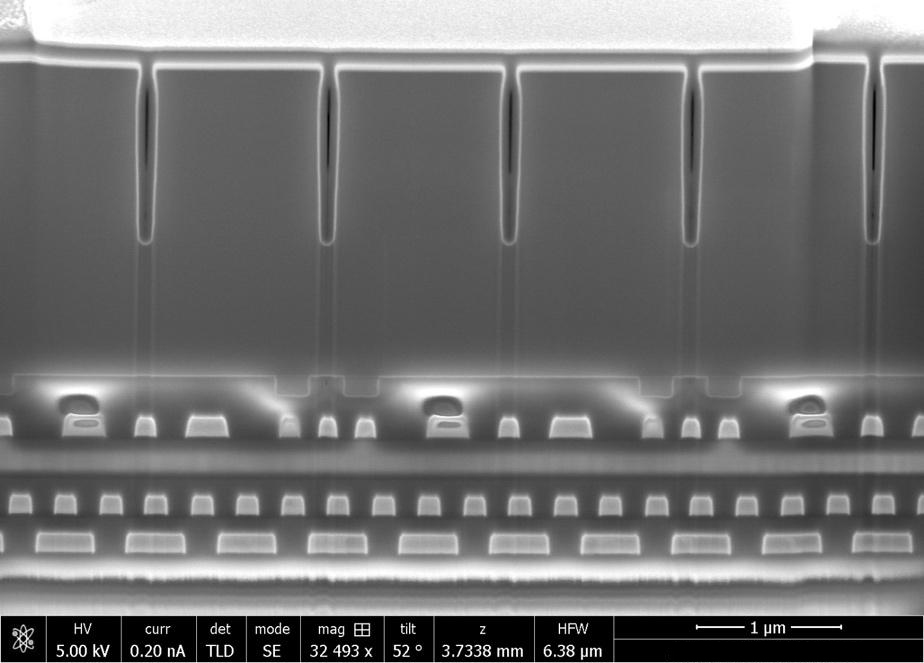
Focused Ion Beam Scanning Electron Microscopy (FIB-SEM)
FIB-SEM systems are used to produce 2D and 3D images of surface topography, and are able to resolve...

Laser Scanning Confocal Microscopy (LSCM)
Laser scanning confocal microscopy (LSCM) is a nondestructive technique which generates 2D and 3D images of a sample...
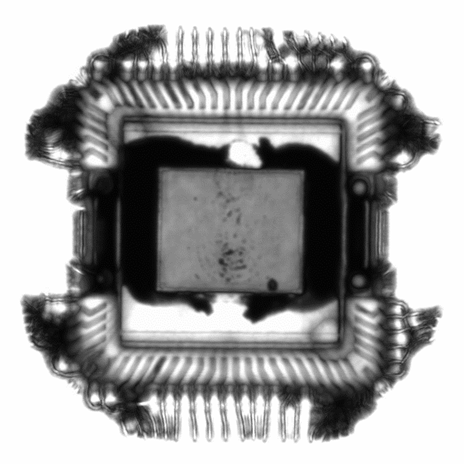
Scanning Acoustic Microscopy (SAM)
Scanning Acoustic Microscopy (SAM) is a non-destructive and non-invasive imaging technique which uses ultrasound signals to visualize the...
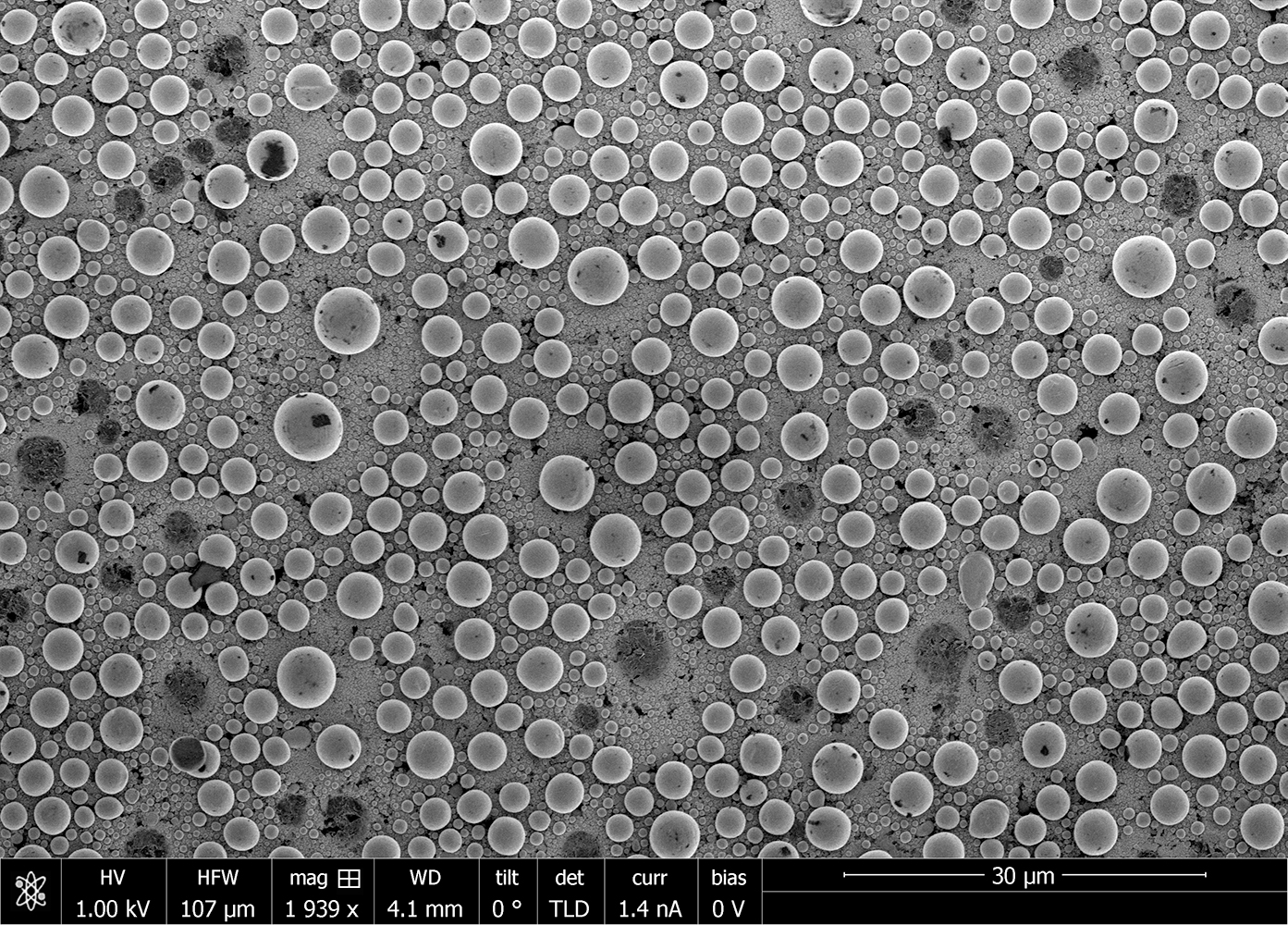

Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) is a surface imaging technique capable of achieving nm resolution on topographical features. Additionally,...
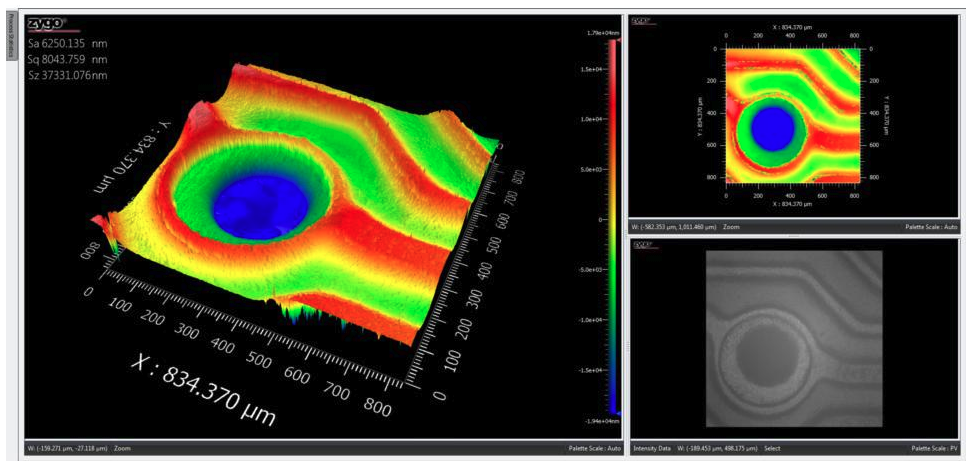
White Light Interferometry (WLI)
White light interferometry (WLI) is a nondestructive, non-contact, optical surface topography measurement which uses coherence scanning interferometry to...

Wide Area 3D Patterned Light Measurement (VR)
Wide Area 3D Patterned Light measurements encompass a class of optical profilometry techniques used to visualize the surface...

X-ray Computed Tomography (Micro-CT)
X-ray computed tomography (often referred to as Micro-CT due to its spatial resolution) is a non-contact, nondestructive 2D...


