Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR)
$99 Base price View My Quote RequestX-ray Computed Tomography (Micro-CT)

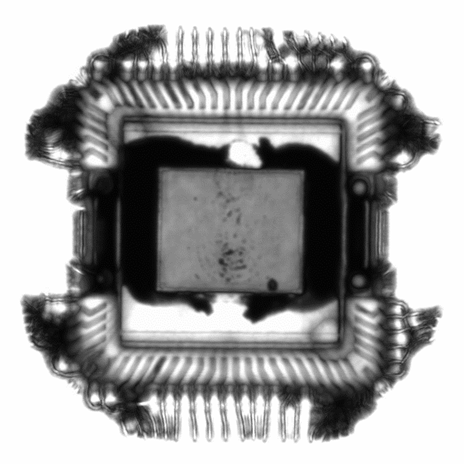
X-ray computed tomography (often referred to as Micro-CT due to its spatial resolution) is a non-contact, nondestructive 2D / 3D imaging technique used to capture morphology and topography at the micron scale of the exterior and interior of the sample.
Covalent uses the best-in-class benchtop Micro-CT instrument, the CT Lab HX130; this is the only HX130 system available for service in North America outside of Rigaku Corp.
- High spatial resolution of 2D images and subsequent 3D models
- Easily accesses interior structures and buried topographies in both industrial and biological samples
- Minimal to no sample preparation is required
- Nondestructive analysis
- Resolution depends on sample size, shape and composition
- Post-processing can take significantly longer than measurement times
Technical Specifications:
Learn More:
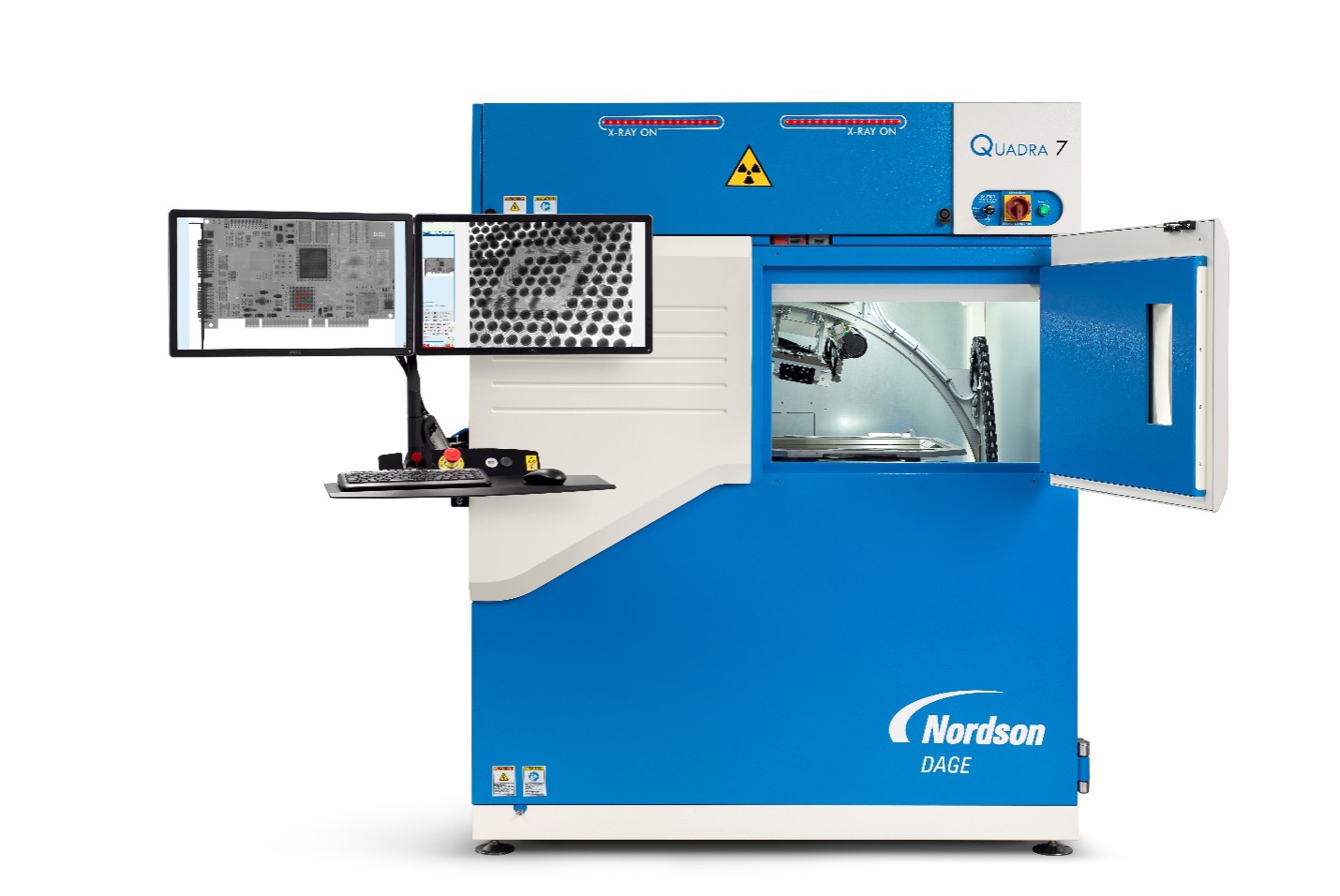

Nordson Dage Quadra 7
- 30-160kV, 20W
- 100nm feature recognition
- 7MP flat panel digital detector
- 30fps framerate
- 0-70° oblique angle view
- 20 x 17.5” inspection area
- Geometric magnification up to 2.5kx & total magnification up to 68kx
- High Dynamic Range (HDR) enhancement software
- X-Plane CT scanning of BGA solder balls
- Dosage control for X-ray sensitive samples
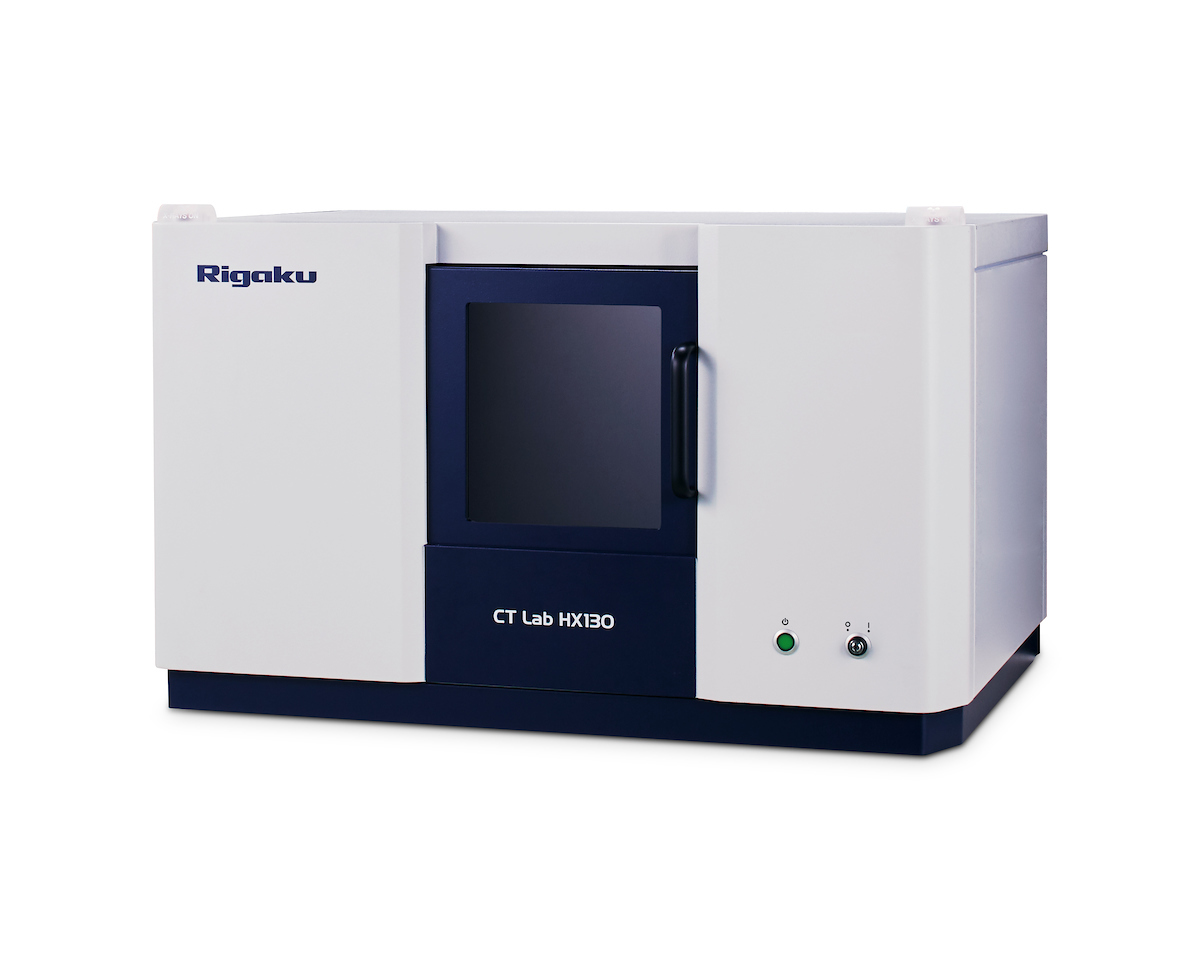

Rigaku CT Lab HX 130
- Field of View: 200 mm
- Spatial Resolution Limit: 5 µm voxel resolution
- X-ray Source Energy: 30 to 130 kV
- X-ray Tube Current: up to 300 uA
View Instrument Spec Sheet
Micro- X-ray Computed Tomography works on the same premise as computed tomography scans in medicine (more commonly called “CT Scans” or “CAT Scans”), but on much smaller analytical volumes.
Tomography encompasses the reconstruction of a 3D model from serial cross-sectional images. In Micro-CT, these cross sections are generated from transmitted X-rays which pass through the sample to reach a 2D area detector.
The system records the intensity of x-ray signal at each pixel in a sensor array, forming a 2D planar projection of the sample’s relative density and material matrix. The resolution and sensitivity of this technique is critically dependent on the detection system and the nature of the sample determines the x-ray beam energy needed. The sample stage is rotated between measurements to produce a series of radial cross sections which the Micro-CT then assembles into a 3D model which can then be quantitatively measured to analyze critical dimensions of surface and subsurface components.
The 3D model contains the full data set of all measurable points within the probed volume, and can be explored virtually to characterize the spatial relations of various features in the sample, to extract 2D images at specific positions and angles, to find hidden differences between seemingly identical samples, and to calculate porosity and other properties: all without damaging or contacting the original sample.

X-ray Radiography Applications

4 Targets for Optimization in a Battery Cell

CT vs SEM: Which is Better?

Batteries Industry Solutions

Datasheet: Medical Device Characterization with the Covalent Platform
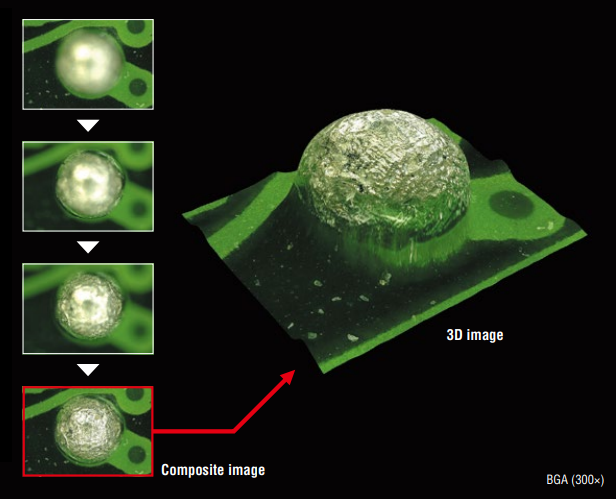
Digital Optical Microscopy (VH Microscope)
Optical microscopy is ubiquitous in diverse fields within academic research and commercial industries. It is an affordable, rapid...
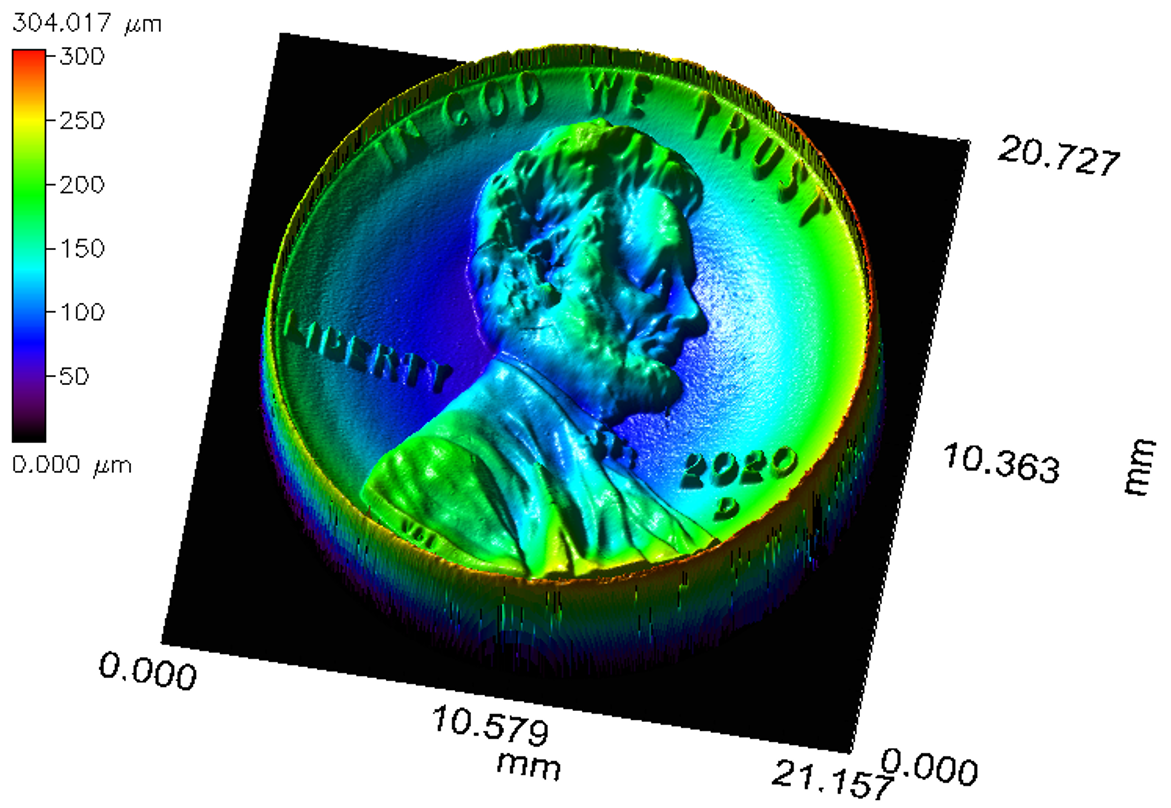
Chromatic Dispersion Profilometry (CWL)
Chromatic dispersion profilometry is a non-contact, nondestructive analytical technique used to measure surface topography. It is particularly well...
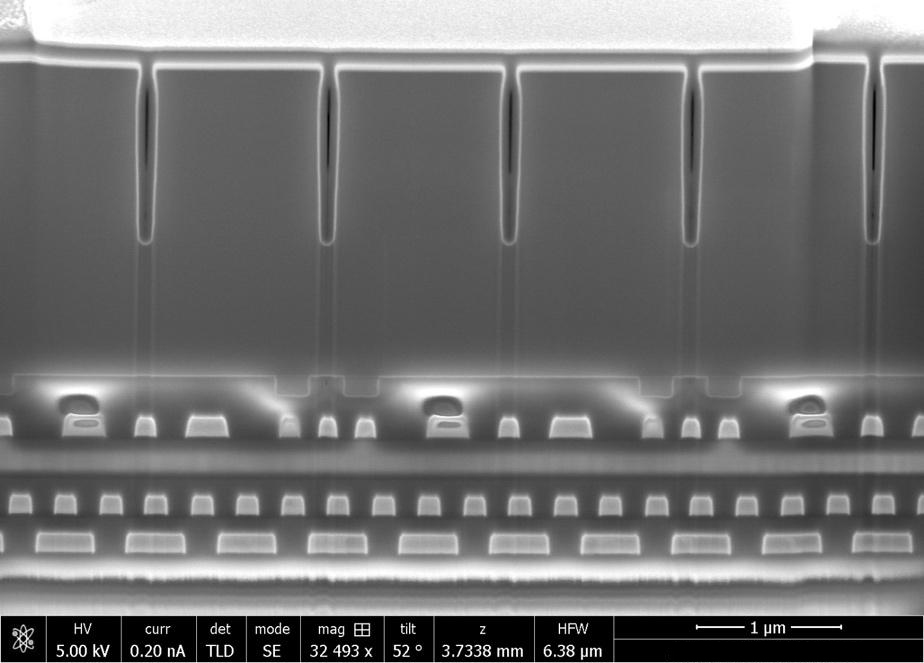
Focused Ion Beam Scanning Electron Microscopy (FIB-SEM)
FIB-SEM systems are used to produce 2D and 3D images of surface topography, and are able to resolve...

Laser Scanning Confocal Microscopy (LSCM)
Laser scanning confocal microscopy (LSCM) is a nondestructive technique which generates 2D and 3D images of a sample...
Scanning Acoustic Microscopy (SAM)
Scanning Acoustic Microscopy (SAM) is a non-destructive and non-invasive imaging technique which uses ultrasound signals to visualize the...
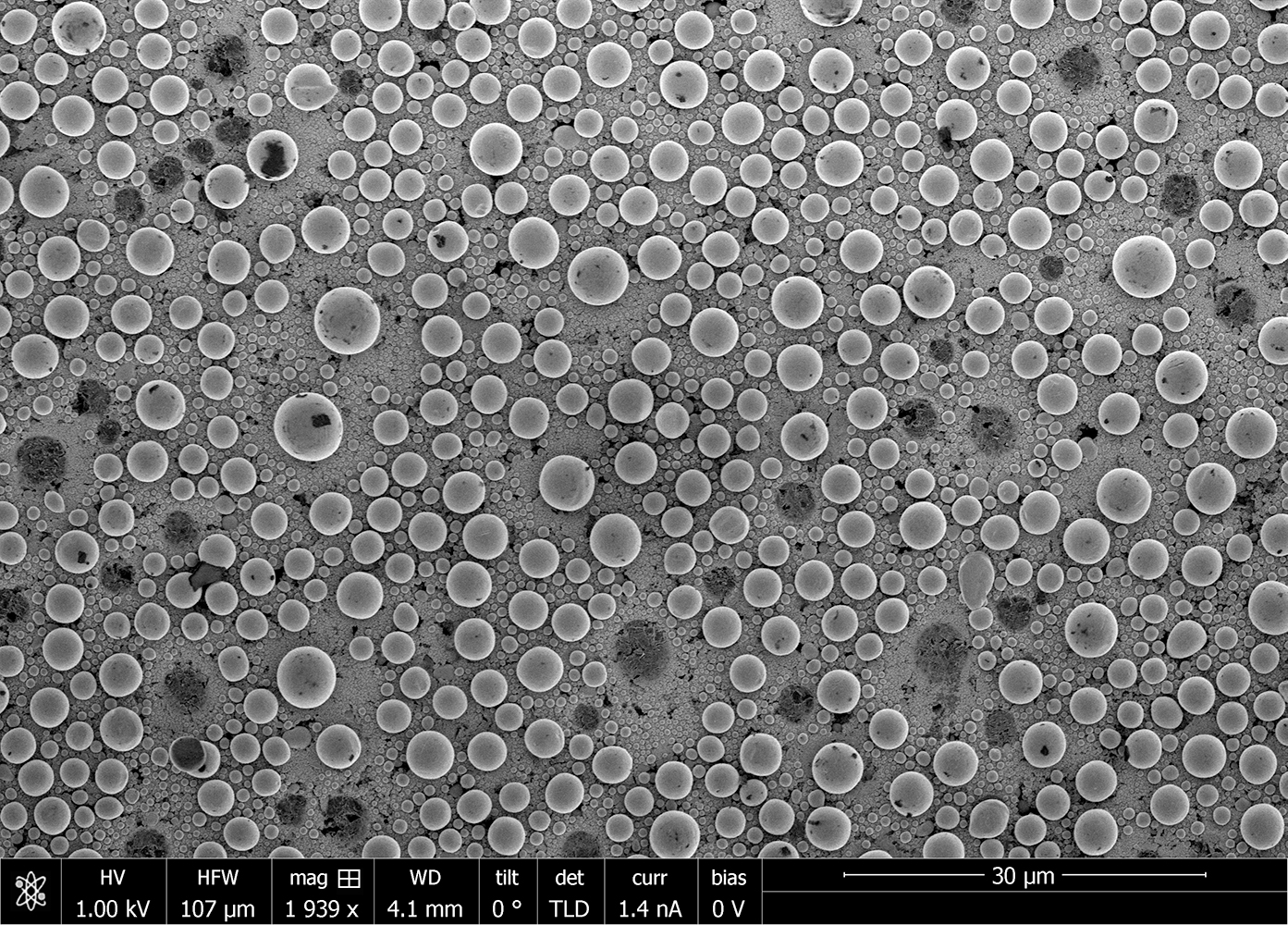

Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) is a surface imaging technique capable of achieving nm resolution on topographical features. Additionally,...